The Obd2 Manual provides comprehensive information on how to use your OBD2 scanner or diagnostic tool, and at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of having access to clear, concise instructions. Our goal is to empower Mercedes-Benz owners and technicians with the knowledge they need to diagnose and maintain their vehicles effectively. Dive into our guide to discover the essentials of OBD2 manuals, diagnostic procedures, and advanced functionalities like unlocking hidden features.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 Manuals
- 1.1 What is an OBD2 Manual?
- 1.2 Why is an OBD2 Manual Important?
- 1.3 Key Components of an OBD2 System
- 1.4 Common Terms and Definitions in OBD2 Manuals
- 1.5 Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 2. Selecting the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
- 2.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 2.2 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Scanner
- 2.3 Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 2.4 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner to Your Vehicle
- 3. Understanding and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.1 What are DTCs?
- 3.2 Common Categories of DTCs
- 3.3 Using an OBD2 Manual to Look Up DTCs
- 3.4 Example DTCs and Their Meanings for Mercedes-Benz
- 3.5 Clearing DTCs
- 4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 4.1 Live Data Streaming
- 4.2 Bi-Directional Control
- 4.3 Actuation Tests
- 4.4 Freeze Frame Data Analysis
- 4.5 Oscilloscope Diagnostics
- 4.6 Mercedes-Benz Specific Diagnostic Procedures
- 5. Unlocking Hidden Features and Customizations on Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 5.1 What are Hidden Features?
- 5.2 Tools Required for Unlocking Hidden Features
- 5.3 Step-by-Step Guide to Unlocking Features
- 5.4 Common Hidden Features to Unlock on Mercedes-Benz
- 5.5 Risks and Precautions
- 6. Performing Routine Maintenance and Repairs Using OBD2 Data
- 6.1 Monitoring Engine Performance
- 6.2 Checking Emission Control Systems
- 6.3 Diagnosing Transmission Problems
- 6.4 Performing Oil Resets and Service Reminders
- 6.5 Using OBD2 Data for Preventive Maintenance
- 7. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
- 7.1 Scanner Not Connecting to Vehicle
- 7.2 Scanner Not Powering On
- 7.3 Incorrect or Incomplete Data
- 7.4 Scanner Freezing or Crashing
- 7.5 Communication Errors
- 8. Legal and Ethical Considerations When Using OBD2 Scanners
- 8.1 Data Privacy
- 8.2 Emissions Regulations
- 8.3 Safety Considerations
- 8.4 Intellectual Property
- 8.5 Professional Ethics
- 9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 9.1 Enhanced Data Collection
- 9.2 Wireless Connectivity
- 9.3 Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities
- 9.4 Integration with Autonomous Vehicles
- 9.5 Cybersecurity
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Manuals
- 10.1 What is the best OBD2 scanner for Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
- 10.2 How do I find the OBD2 port in my Mercedes-Benz?
- 10.3 Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my Mercedes-Benz?
- 10.4 How do I update the software on my OBD2 scanner?
- 10.5 What do I do if my OBD2 scanner is not connecting to my vehicle?
- 10.6 Can I unlock hidden features on my Mercedes-Benz with an OBD2 scanner?
- 10.7 Is it safe to clear DTCs without fixing the problem?
- 10.8 How often should I use my OBD2 scanner?
- 10.9 What are the legal considerations when using an OBD2 scanner?
- 10.10 Where can I find reliable OBD2 manuals and resources?
1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 Manuals
OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) manuals are essential guides for understanding and using OBD2 scanners, which are vital tools for diagnosing vehicle problems. These manuals provide detailed information on how to interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), perform tests, and understand vehicle data. Let’s delve into the core aspects of OBD2 manuals:
1.1 What is an OBD2 Manual?
An OBD2 manual is a comprehensive guide that explains how to use an OBD2 scanner. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks manufactured after 1996 are required to have an OBD2 system. The manual typically covers:
- Scanner Features: Explains the functions and capabilities of the scanner.
- DTCs: Lists and explains diagnostic trouble codes, helping users understand what each code means.
- Testing Procedures: Provides step-by-step instructions on how to perform various diagnostic tests.
- Data Interpretation: Guides users on how to interpret the data provided by the scanner.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Offers advice on common issues and how to resolve them.
1.2 Why is an OBD2 Manual Important?
Having an OBD2 manual is essential for several reasons. First, it enables vehicle owners to diagnose problems themselves, potentially saving money on mechanic fees. Second, it provides a deeper understanding of how the vehicle operates, leading to better maintenance practices. Third, it helps technicians accurately diagnose and repair vehicles, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
1.3 Key Components of an OBD2 System
To fully utilize an OBD2 manual, understanding the key components of the OBD2 system is important. These include:
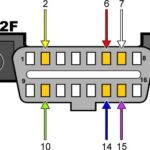
- OBD2 Port: The diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard, where the scanner connects.
- Sensors: Various sensors throughout the vehicle that monitor engine performance, emissions, and other critical functions.
- ECU (Engine Control Unit): The vehicle’s computer that receives data from the sensors and controls various systems.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Codes generated by the ECU when a problem is detected.
1.4 Common Terms and Definitions in OBD2 Manuals
OBD2 manuals often include technical terms that can be confusing for beginners. Here are some common definitions:
- PID (Parameter Identification): A code used to request data from the ECU, such as engine speed or coolant temperature.
- Freeze Frame Data: A snapshot of the vehicle’s data at the moment a DTC was triggered.
- Live Data: Real-time data from the vehicle’s sensors, allowing users to monitor performance.
- MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp): The check engine light that illuminates when a problem is detected.
1.5 Benefits of Using an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner, as detailed in the manual, offers numerous advantages:
- Early Problem Detection: Identifies issues before they become major problems.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for expensive mechanic visits for simple diagnoses.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Helps maintain optimal engine performance, improving fuel economy.
- Enhanced Vehicle Performance: Ensures all systems are running correctly, enhancing overall performance.
- Environmental Benefits: Monitors emissions and ensures the vehicle is not polluting excessively.
2. Selecting the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Needs
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics. The market offers a wide range of scanners, each with different features and capabilities. Here’s a guide to help you select the best tool for your specific needs:
2.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners
There are several types of OBD2 scanners available, each designed for different users and purposes:
- Basic OBD2 Scanners: These are simple, handheld devices that read and clear DTCs. They are suitable for basic troubleshooting and are often the most affordable option.
- Mid-Range Scanners: These scanners offer additional features such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and the ability to perform some basic tests. They are ideal for DIY enthusiasts and some professional technicians.
- Advanced Scanners: These are sophisticated tools that offer advanced features such as bi-directional control, module programming, and access to manufacturer-specific codes. They are typically used by professional technicians in repair shops.
- Smartphone-Based Scanners: These devices connect to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi and use an app to display diagnostic information. They are often portable and user-friendly.
2.2 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Scanner
When selecting an OBD2 scanner, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Some scanners are designed for specific brands. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we specialize in tools optimized for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Features: Determine the features you need. If you only need to read and clear codes, a basic scanner will suffice. For more advanced diagnostics, consider a scanner with live data and bi-directional control.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with a user-friendly interface. A clear display and intuitive menu system can make the diagnostic process much easier.
- Price: Set a budget and find a scanner that offers the best value for your money. Keep in mind that more expensive scanners often come with more features and capabilities.
- Updates: Check if the scanner supports software updates. Regular updates ensure the scanner can diagnose the latest vehicle models and access the most recent DTCs.
- Reviews: Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the scanner’s reliability and performance.
2.3 Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
For Mercedes-Benz vehicles, consider these scanners:
| Scanner | Features | User Level |
|---|---|---|
| iCarsoft MB V3.0 | Full system diagnosis, oil reset, EPB reset, SAS reset, battery reset, DPF regeneration, injector coding. | DIY Enthusiast |
| Autel MaxiCOM MK808 | Full system diagnosis, bi-directional control, key coding, ABS bleeding, oil reset, EPB reset, TPMS reset. | DIY to Pro |
| Launch X431 V+ | Full system diagnosis, bi-directional control, ECU coding, key programming, advanced service functions. | Professional |
| Mercedes Star C4/C5/C6 | Dealer-level diagnostics, ECU programming, SCN coding, full access to Mercedes-Benz diagnostic functions. | Professional |
| Foxwell NT530 | Compatible with multiple makes, but also allows you access to deeper systems in Mercedes, live data, actuation tests, oil light resets, and throttle body alignments. | DIY Enthusiastic |
2.4 Connecting the OBD2 Scanner to Your Vehicle
Connecting an OBD2 scanner to your vehicle is a simple process:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: It’s usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the scanner to the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: The scanner should power on automatically. If not, press the power button.
- Follow the Instructions: Use the scanner’s menu to perform the desired diagnostic tests.
3. Understanding and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes generated by your vehicle’s computer (ECU) when it detects a problem. Understanding and interpreting these codes is essential for effective vehicle diagnostics.
3.1 What are DTCs?
DTCs are alphanumeric codes that indicate a specific problem in your vehicle. These codes are standardized across the automotive industry, but some manufacturers also have their own proprietary codes. DTCs typically consist of five characters:
- First Character: Indicates the system (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network).
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Third Character: Indicates the specific system or component that is experiencing the problem (e.g., Fuel System, Ignition System, Emission Control).
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Provide more specific information about the problem.
3.2 Common Categories of DTCs
DTCs are categorized based on the system they relate to:
- P Codes (Powertrain): These codes relate to the engine, transmission, and related components. Examples include P0300 (Random Misfire Detected) and P0171 (System Too Lean).
- B Codes (Body): These codes relate to the body of the vehicle, including the doors, windows, and seats. Examples include B1001 (Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Hardware Failure) and B2206 (Lost Communication with Front Display Interface Module).
- C Codes (Chassis): These codes relate to the chassis of the vehicle, including the brakes, suspension, and steering. Examples include C0031 (Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit) and C0040 (Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit).
- U Codes (Network): These codes relate to the vehicle’s communication network, including the CAN bus. Examples include U0100 (Lost Communication with ECM/PCM) and U0155 (Lost Communication with Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC) Control Module).
3.3 Using an OBD2 Manual to Look Up DTCs
An OBD2 manual provides a comprehensive list of DTCs and their definitions. To look up a DTC:
- Read the Code: Use the OBD2 scanner to read the DTC.
- Consult the Manual: Find the code in the manual’s DTC list.
- Understand the Definition: Read the definition of the code to understand the problem.
- Check Possible Causes: The manual usually lists possible causes for each code.
- Perform Diagnostic Tests: Follow the manual’s instructions to perform diagnostic tests and confirm the problem.
3.4 Example DTCs and Their Meanings for Mercedes-Benz
Here are some example DTCs specific to Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
| DTC | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0016 | Crankshaft Position – Camshaft Position Correlation | Faulty camshaft position sensor, faulty crankshaft position sensor, timing chain stretched, timing chain misaligned. |
| P0102 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Circuit Low Input | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, intake air leaks, wiring problems. |
| P0170 | Fuel Trim Malfunction (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, faulty fuel injectors, low fuel pressure. |
| C1000 | BAS (Brake Assist System) Control Module Fault | Faulty BAS control module, wiring problems, low battery voltage. |
| B1010 | Component N70 (Overhead Control Panel Control Unit) is not sending data | Wiring fault, faulty overhead control panel control unit, CAN bus communication failure. |
3.5 Clearing DTCs
After diagnosing and repairing the problem, you need to clear the DTC. Here’s how:
- Repair the Issue: Ensure the problem has been fixed before clearing the code.
- Connect the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the vehicle.
- Clear the Code: Use the scanner’s menu to clear the DTC.
- Verify the Repair: Start the vehicle and check if the code returns. If it does, the problem has not been fully resolved.
4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Advanced diagnostic techniques are essential for accurately diagnosing complex issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These techniques go beyond basic code reading and require a deeper understanding of the vehicle’s systems.
4.1 Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming allows you to monitor real-time data from the vehicle’s sensors. This can help you identify intermittent problems and diagnose issues that don’t trigger DTCs. Key parameters to monitor include:
- Engine Speed (RPM): Indicates how fast the engine is running.
- Coolant Temperature: Monitors the engine’s operating temperature.
- Fuel Trim: Indicates how the ECU is adjusting the fuel mixture.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Monitors the performance of the oxygen sensors.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF): Measures the amount of air entering the engine.
By analyzing these parameters, you can identify problems such as vacuum leaks, faulty sensors, and fuel delivery issues.
4.2 Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s systems and observe their response. This can help you test components such as fuel injectors, solenoids, and relays. For example, you can use bi-directional control to:
- Activate Fuel Injectors: Test if the injectors are firing correctly.
- Cycle ABS Pump: Bleed the ABS system.
- Control Cooling Fans: Test if the cooling fans are operating properly.
- Actuate Throttle Body: Test the throttle body’s response.
4.3 Actuation Tests
Actuation tests involve activating specific components to verify their functionality. These tests can help you diagnose problems with:
- EGR Valve: Test if the EGR valve is opening and closing correctly.
- Purge Valve: Test if the purge valve is controlling fuel vapor flow.
- Variable Valve Timing (VVT): Test if the VVT system is adjusting valve timing properly.
4.4 Freeze Frame Data Analysis
Freeze frame data provides a snapshot of the vehicle’s data at the moment a DTC was triggered. This can help you understand the conditions that led to the problem. Key data points to analyze include:
- Engine Load: Indicates how hard the engine was working.
- Vehicle Speed: Shows the speed of the vehicle.
- Fuel Trim: Indicates the fuel mixture at the time of the fault.
- Coolant Temperature: Shows the engine temperature.
4.5 Oscilloscope Diagnostics
An oscilloscope is a powerful tool for analyzing electrical signals in your vehicle. It can help you diagnose problems with sensors, actuators, and wiring. For example, you can use an oscilloscope to:
- Test Crankshaft and Camshaft Sensors: Verify the signal patterns of these sensors.
- Analyze Fuel Injector Waveforms: Check the performance of the fuel injectors.
- Diagnose Wiring Problems: Identify shorts, opens, and other wiring issues.
4.6 Mercedes-Benz Specific Diagnostic Procedures
Mercedes-Benz vehicles often require specific diagnostic procedures due to their advanced technology. These procedures may include:
- SCN Coding: Programming control units with the correct software and configuration.
- Variant Coding: Configuring control units for specific vehicle options.
- Adaptations: Teaching control units new values, such as throttle position or idle speed.
5. Unlocking Hidden Features and Customizations on Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Many Mercedes-Benz vehicles have hidden features that can be unlocked through coding and programming. These features can enhance the vehicle’s functionality and personalize the driving experience.
5.1 What are Hidden Features?
Hidden features are functions or settings that are present in the vehicle’s software but are not activated by default. These features can include:
- Ambient Lighting Customization: Adjusting the colors and intensity of the ambient lighting.
- Performance Displays: Enabling additional performance data on the instrument cluster.
- Comfort Features: Activating features such as automatic door locking and unlocking.
- Lighting Enhancements: Customizing the behavior of the headlights and taillights.
- Acoustic Enhancements: Fine-tuning exhaust sound.
5.2 Tools Required for Unlocking Hidden Features
To unlock hidden features, you will need the right tools and software:
- OBD2 Scanner: A scanner that supports coding and programming.
- Coding Software: Software such as Vediamo, DTS Monaco, or XENTRY Developer.
- Laptop: A laptop with the necessary software installed.
- Stable Power Supply: A power supply to maintain voltage during coding.
5.3 Step-by-Step Guide to Unlocking Features
Here’s a general guide to unlocking hidden features on Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
- Connect the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the vehicle.
- Start the Coding Software: Launch the coding software on your laptop.
- Select the Control Unit: Identify the control unit that contains the feature you want to unlock (e.g., Instrument Cluster, Central Gateway).
- Read the Current Configuration: Read the current configuration of the control unit.
- Modify the Configuration: Change the necessary parameters to activate the hidden feature.
- Write the New Configuration: Write the new configuration to the control unit.
- Verify the Changes: Test the new feature to ensure it is working correctly.
5.4 Common Hidden Features to Unlock on Mercedes-Benz
Some popular hidden features to unlock include:
- AMG Menu in Instrument Cluster: Displays additional performance data such as engine oil temperature and boost pressure.
- Enhanced Ambient Lighting: Allows for more customization options for the ambient lighting.
- Sport Displays: Activates sportier displays in the instrument cluster.
- Acoustic Feedback: Modifying the exhaust sound.
- Video in Motion: Enables video playback on the infotainment system while driving.
5.5 Risks and Precautions
Unlocking hidden features can be risky if not done correctly. It’s important to:
- Back Up the Original Configuration: Always back up the original configuration before making any changes.
- Use Reliable Software: Use reliable and tested coding software.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Follow the instructions in the OBD2 manual and coding guides.
- Maintain a Stable Power Supply: Ensure the vehicle has a stable power supply to prevent data corruption.
- Seek Professional Help: If you are not comfortable with coding, seek help from a professional.
6. Performing Routine Maintenance and Repairs Using OBD2 Data
Using OBD2 data, detailed in your OBD2 manual, can greatly improve your routine maintenance and repair tasks. By monitoring vehicle data, you can identify potential problems early and perform preventive maintenance.
6.1 Monitoring Engine Performance
OBD2 data can help you monitor engine performance and identify issues such as:
- Misfires: Detect misfires by monitoring the misfire counters.
- Fuel Trim Issues: Identify lean or rich conditions by monitoring fuel trim values.
- Oxygen Sensor Problems: Check the performance of the oxygen sensors.
- MAF Sensor Problems: Monitor the MAF sensor readings to ensure proper air flow.
6.2 Checking Emission Control Systems
OBD2 data can help you check the emission control systems and ensure they are functioning correctly:
- Catalytic Converter Efficiency: Monitor the catalytic converter efficiency to ensure it is reducing emissions.
- EGR System Performance: Check the EGR valve operation and flow.
- EVAP System Performance: Monitor the EVAP system for leaks and proper operation.
6.3 Diagnosing Transmission Problems
OBD2 data can help you diagnose transmission problems by monitoring:
- Transmission Temperature: Ensure the transmission is not overheating.
- Shift Solenoid Operation: Check the operation of the shift solenoids.
- Torque Converter Lockup: Monitor the torque converter lockup function.
6.4 Performing Oil Resets and Service Reminders
Many OBD2 scanners can perform oil resets and reset service reminders. This is a simple process:
- Connect the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the vehicle.
- Select Service Functions: Navigate to the service functions menu.
- Perform Oil Reset: Follow the instructions to reset the oil service interval.
- Reset Service Reminders: Reset any other service reminders as needed.
6.5 Using OBD2 Data for Preventive Maintenance
OBD2 data can be used for preventive maintenance by:
- Regularly Monitoring Vehicle Data: Check for any abnormalities in the data.
- Performing Scheduled Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule.
- Addressing Issues Early: Fix any problems identified by the OBD2 scanner before they become major issues.
7. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Scanner Issues
While OBD2 scanners are valuable tools, they can sometimes encounter issues. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
7.1 Scanner Not Connecting to Vehicle
If the scanner is not connecting to the vehicle:
- Check the Connection: Ensure the scanner is properly plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Verify Compatibility: Make sure the scanner is compatible with the vehicle.
- Check the OBD2 Port: Inspect the OBD2 port for damage or corrosion.
- Test with Another Vehicle: Try the scanner on another vehicle to see if the problem is with the scanner or the vehicle.
7.2 Scanner Not Powering On
If the scanner is not powering on:
- Check the Power Source: Ensure the vehicle’s ignition is turned on.
- Check the Scanner’s Batteries: Replace the batteries if necessary.
- Test the Scanner’s Power Adapter: If the scanner uses a power adapter, test it to ensure it is working.
7.3 Incorrect or Incomplete Data
If the scanner is displaying incorrect or incomplete data:
- Update the Scanner’s Software: Ensure the scanner has the latest software updates.
- Verify the Vehicle Information: Make sure the scanner has the correct vehicle information.
- Check the Sensors: Test the vehicle’s sensors to ensure they are functioning correctly.
7.4 Scanner Freezing or Crashing
If the scanner is freezing or crashing:
- Restart the Scanner: Try restarting the scanner.
- Clear the Scanner’s Memory: Clear the scanner’s memory to free up resources.
- Update the Scanner’s Software: Install the latest software updates.
7.5 Communication Errors
If the scanner is displaying communication errors:
- Check the Wiring: Inspect the wiring between the scanner and the vehicle for damage.
- Verify the Protocol: Ensure the scanner is using the correct communication protocol.
- Test with Another Scanner: Try another scanner to see if the problem is with the scanner or the vehicle.
8. Legal and Ethical Considerations When Using OBD2 Scanners
Using OBD2 scanners involves certain legal and ethical considerations. It’s important to be aware of these to ensure you are using the scanner responsibly.
8.1 Data Privacy
OBD2 scanners can access and store vehicle data, including personal information. It’s important to:
- Protect Personal Information: Securely store and protect any personal information collected by the scanner.
- Comply with Privacy Laws: Adhere to all applicable privacy laws and regulations.
- Inform Vehicle Owners: Inform vehicle owners about the data being collected and how it will be used.
8.2 Emissions Regulations
OBD2 scanners are used to monitor emissions and ensure vehicles comply with regulations. It’s important to:
- Comply with Emissions Standards: Ensure the vehicle meets all applicable emissions standards.
- Avoid Tampering: Do not tamper with the emission control systems or disable any emission-related functions.
- Report Violations: Report any violations of emissions regulations to the appropriate authorities.
8.3 Safety Considerations
Using OBD2 scanners can involve safety risks, especially when performing diagnostic tests while the vehicle is running. It’s important to:
- Follow Safety Procedures: Follow all safety procedures and guidelines.
- Use Protective Equipment: Wear appropriate protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses.
- Work in a Safe Environment: Perform diagnostic tests in a safe and well-ventilated environment.
8.4 Intellectual Property
OBD2 scanners and coding software may be protected by intellectual property laws. It’s important to:
- Respect Copyrights: Respect the copyrights and intellectual property rights of software and hardware manufacturers.
- Avoid Piracy: Do not use pirated or unauthorized software.
- Obtain Licenses: Obtain the necessary licenses for any software or hardware used.
8.5 Professional Ethics
For professional technicians, it’s important to adhere to ethical standards when using OBD2 scanners:
- Provide Accurate Diagnoses: Provide accurate and honest diagnoses.
- Avoid Unnecessary Repairs: Do not perform unnecessary repairs or services.
- Maintain Confidentiality: Maintain the confidentiality of customer information.
- Act with Integrity: Act with integrity and honesty in all professional dealings.
9. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology continues to evolve, with new features and capabilities being developed. Here are some trends to watch:
9.1 Enhanced Data Collection
Future OBD2 systems will collect more data than ever before, providing a more comprehensive view of vehicle performance. This data can be used for:
- Predictive Maintenance: Predicting when components are likely to fail.
- Remote Diagnostics: Diagnosing problems remotely.
- Improved Vehicle Performance: Optimizing vehicle performance based on real-world data.
9.2 Wireless Connectivity
Wireless connectivity will become more common, allowing OBD2 scanners to connect to vehicles via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. This will make it easier to:
- Access Data Remotely: Access vehicle data from anywhere.
- Update Software Over-the-Air: Update scanner software wirelessly.
- Integrate with Mobile Apps: Integrate with mobile apps for enhanced functionality.
9.3 Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities
Future OBD2 scanners will offer more advanced diagnostic capabilities, such as:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Using AI to analyze data and provide more accurate diagnoses.
- Machine Learning (ML): Using ML to learn from vehicle data and improve diagnostic accuracy.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Storing and analyzing data in the cloud for enhanced performance.
9.4 Integration with Autonomous Vehicles
OBD2 technology will play a critical role in autonomous vehicles, providing data for:
- Vehicle Health Monitoring: Monitoring the health of the vehicle’s systems.
- Remote Control: Controlling the vehicle remotely.
- Safety Systems: Enhancing the safety systems of autonomous vehicles.
9.5 Cybersecurity
As OBD2 systems become more connected, cybersecurity will become increasingly important. Future systems will need to:
- Protect Against Hacking: Protect against unauthorized access and hacking.
- Secure Data Transmission: Securely transmit data to prevent interception.
- Implement Authentication: Implement strong authentication measures to verify users.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Manuals
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 manuals and scanners:
10.1 What is the best OBD2 scanner for Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
The best OBD2 scanner for Mercedes-Benz vehicles depends on your needs and budget. Some popular options include the iCarsoft MB V3.0, Autel MaxiCOM MK808, and Launch X431 V+.
10.2 How do I find the OBD2 port in my Mercedes-Benz?
The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your vehicle’s manual for the exact location.
10.3 Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my Mercedes-Benz?
While most OBD2 scanners will work, some are better suited for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Look for scanners that support Mercedes-Benz specific codes and functions.
10.4 How do I update the software on my OBD2 scanner?
The process for updating the software varies depending on the scanner. Consult your scanner’s manual for instructions.
10.5 What do I do if my OBD2 scanner is not connecting to my vehicle?
Check the connection, verify compatibility, inspect the OBD2 port, and try the scanner on another vehicle.
10.6 Can I unlock hidden features on my Mercedes-Benz with an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, but you will need a scanner that supports coding and programming, as well as the necessary software.
10.7 Is it safe to clear DTCs without fixing the problem?
No, it is not safe to clear DTCs without fixing the problem. The code will likely return, and the underlying issue will remain unresolved.
10.8 How often should I use my OBD2 scanner?
You can use your OBD2 scanner as often as you like to monitor vehicle performance and identify potential problems.
10.9 What are the legal considerations when using an OBD2 scanner?
Be aware of data privacy, emissions regulations, safety considerations, and intellectual property laws.
10.10 Where can I find reliable OBD2 manuals and resources?
You can find reliable OBD2 manuals and resources at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, as well as from reputable automotive websites and manufacturers.
By understanding and utilizing the information in your OBD2 manual, you can effectively diagnose, maintain, and customize your Mercedes-Benz vehicle. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional technician, having access to the right tools and knowledge is essential for keeping your vehicle running smoothly.
Need expert advice on choosing the right diagnostic tools, unlocking hidden features, or performing advanced repairs on your Mercedes-Benz? Contact us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today!
Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Let us help you take the best care of your Mercedes-Benz!