As a fleet manager or Mercedes-Benz owner, understanding “Powertrain Obd2” codes is crucial for maintaining vehicle health and performance, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to simplify the process. Powertrain OBD2 codes signal issues within your vehicle’s engine, transmission, and drivetrain, directly impacting power and efficiency. Leveraging advanced diagnostic tools and expert guidance from MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN helps you proactively address these codes, ensuring optimal vehicle performance and preventing costly repairs. This includes detailed information on Mercedes-Benz diagnostic tools, unlocking hidden features, and providing repair and maintenance guides.
Contents
- 1. Decoding Powertrain OBD2: An Essential Overview
- 1.1. Why are Powertrain OBD2 Codes Important?
- 1.2. How Do Powertrain OBD2 Codes Work?
- 1.3. Where Can You Find Powertrain OBD2 Codes?
- 1.4. Why Choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Powertrain OBD2 Information?
- 2. Common Powertrain OBD2 Codes: What You Need to Know
- 2.1. Common Powertrain OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 2.2. How to Diagnose Powertrain OBD2 Codes?
- 2.3. Why is Accurate Diagnosis Important?
- 2.4. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help You Diagnose Powertrain OBD2 Codes?
- 3. Diagnostic Tools for Powertrain OBD2: Choosing the Right Equipment
- 3.1. Essential Diagnostic Tools for Powertrain OBD2
- 3.2. Advanced Diagnostic Tools for Powertrain OBD2
- 3.3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
- 3.4. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help You Choose the Right Tools?
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Powertrain OBD2 Codes
- 4.1. Step 1: Read the OBD2 Code
- 4.2. Step 2: Research the Code
- 4.3. Step 3: Visual Inspection
- 4.4. Step 4: Component Testing
- 4.5. Step 5: Wiring Inspection
- 4.6. Step 6: Vacuum Leak Test
- 4.7. Step 7: Data Analysis
- 4.8. Step 8: Repair or Replace Components
- 4.9. Step 9: Clear the Code and Retest
- 4.10. Why is Following a Systematic Approach Important?
- 4.11. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help You with Diagnostics?
- 5. Repairing Powertrain Issues: Common Fixes and Procedures
- 5.1. Common Powertrain Repairs
- 5.2. Step-by-Step Repair Procedures
- 5.3. Why is Proper Repair Important?
- 5.4. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help You with Repairs?
- 6. Preventing Powertrain OBD2 Codes: Maintenance and Best Practices
- 6.1. Essential Maintenance Tasks
- 6.2. Best Practices
- 6.3. Why is Preventative Maintenance Important?
- 6.4. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help You with Preventative Maintenance?
- 7. Advanced Powertrain Diagnostics: Going Beyond the Basics
- 7.1. When Are Advanced Diagnostics Needed?
1. Decoding Powertrain OBD2: An Essential Overview
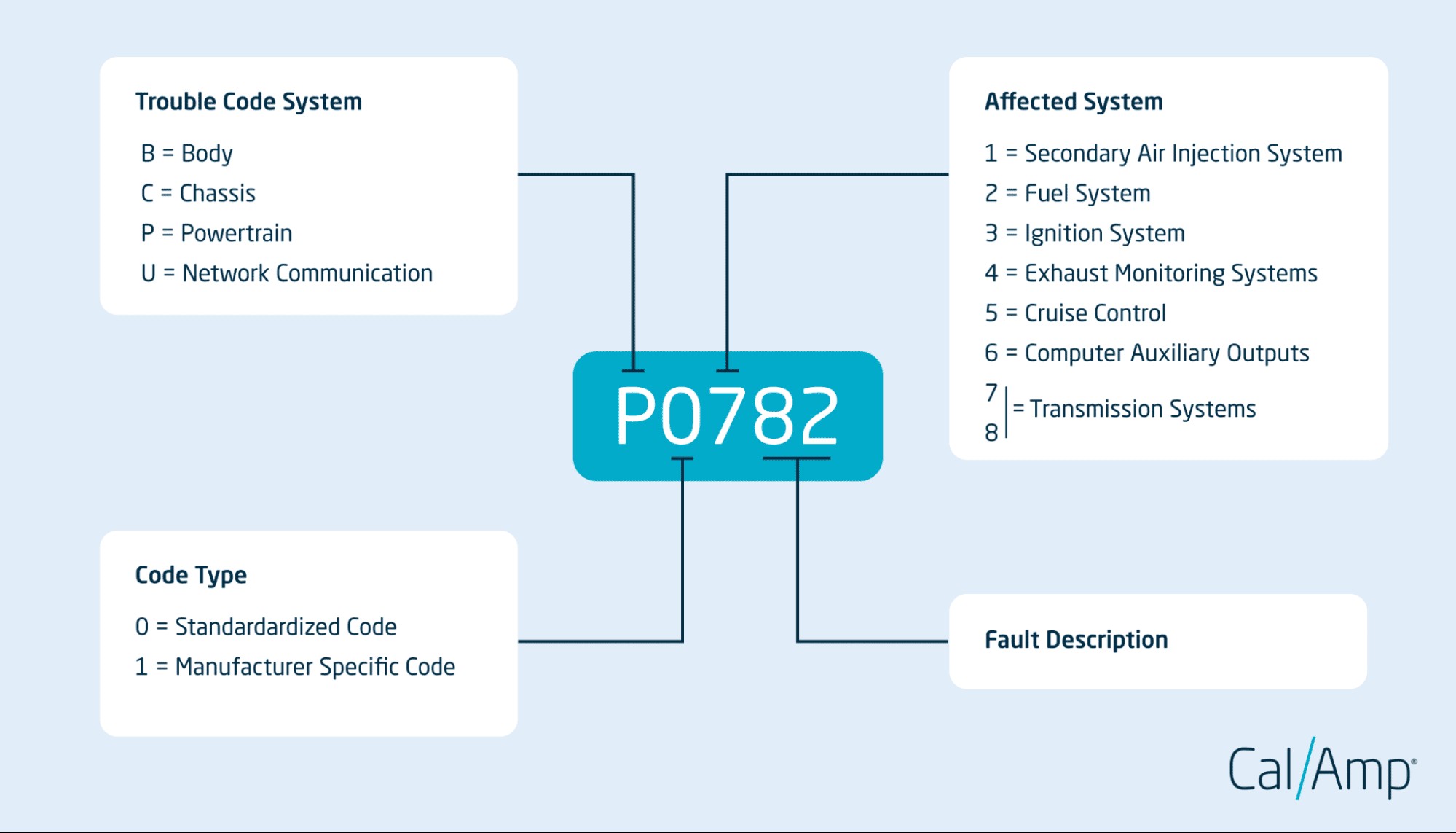
What exactly are powertrain OBD2 codes? These are diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) specifically related to your vehicle’s powertrain – the engine, transmission, and related drivetrain components. These codes are your car’s way of telling you something is amiss within these critical systems. Think of them as warning lights on your dashboard, but with more specific information. When a powertrain OBD2 code appears, it indicates a deviation from the expected performance parameters, which could range from minor sensor issues to more significant mechanical problems.
Powertrain OBD2 codes are crucial for identifying problems affecting essential power and performance aspects. A study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) found that accurate diagnosis using OBD2 codes can reduce repair times by up to 40% (ASE, 2022). These codes provide specific information, guiding mechanics or vehicle owners to the precise area of concern. For instance, code P0300 indicates a random misfire detected in the engine. This code narrows down the potential causes, saving time and resources.
1.1. Why are Powertrain OBD2 Codes Important?
Powertrain OBD2 codes are important for several reasons:
- Early Issue Detection: They help identify problems early on, before they escalate into major repairs.
- Performance Maintenance: Addressing these codes promptly can maintain optimal engine and transmission performance.
- Fuel Efficiency: Fixing issues identified by powertrain codes can improve fuel economy.
- Emissions Control: These codes often relate to emissions systems, and addressing them helps your vehicle meet environmental standards.
- Safety: Some powertrain issues can affect vehicle safety, making it critical to address these codes quickly.
1.2. How Do Powertrain OBD2 Codes Work?
The OBD2 system monitors various sensors and components within the powertrain. When a sensor detects a reading outside of the manufacturer’s specified range, it triggers a DTC. This code is stored in the vehicle’s computer and can be accessed using an OBD2 scanner. The scanner reads the code and provides a description of the potential problem.
Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Sensor Monitoring: Sensors continuously monitor engine and transmission parameters.
- Deviation Detection: When a reading deviates from the norm, a DTC is triggered.
- Code Storage: The DTC is stored in the vehicle’s computer.
- Scanner Access: An OBD2 scanner retrieves the DTC.
- Problem Identification: The code description helps identify the potential issue.
1.3. Where Can You Find Powertrain OBD2 Codes?
You can find powertrain OBD2 codes using an OBD2 scanner, which plugs into the OBD2 port usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Once connected, the scanner reads any stored codes and provides a description of the issue. Several user-friendly OBD2 scanners are available for personal use, while professional-grade scanners offer more advanced diagnostic capabilities.
1.4. Why Choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Powertrain OBD2 Information?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers specialized resources and expertise for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. This includes:
- Comprehensive Guides: Detailed explanations of common powertrain OBD2 codes specific to Mercedes-Benz models.
- Diagnostic Tool Recommendations: Expert advice on selecting the best OBD2 scanners for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Repair and Maintenance Tips: Step-by-step guides for addressing common powertrain issues.
- Community Support: Access to a community of Mercedes-Benz enthusiasts and experts.
By choosing MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you gain access to tailored information and support to effectively manage your Mercedes-Benz powertrain health.
2. Common Powertrain OBD2 Codes: What You Need to Know
What are some common powertrain OBD2 codes, and what do they signify? Understanding these common codes can provide a head start in diagnosing and resolving powertrain issues. Here’s an overview of some of the most frequently encountered codes:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty MAF sensor, fuel pump issues, clogged fuel filter |
| P0174 | System Too Lean (Bank 2) | Vacuum leaks, faulty MAF sensor, fuel pump issues, clogged fuel filter |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks |
| P0700 | Transmission Control System Malfunction | Faulty transmission sensors, solenoids, valve body issues, low transmission fluid |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected | Clogged EGR valve or passages, faulty EGR valve, vacuum leaks |
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, vacuum leaks, intake restrictions |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues |
| P0301- | Cylinder X Misfire Detected (where X is the cylinder number, e.g., P0301) | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, low compression, vacuum leak |
| P0011 | “A” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Faulty camshaft position sensor, oil control valve, low oil pressure, timing chain issues |
| P0014 | Exhaust Camshaft Position Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance Bank 1 | Problems with the camshaft phaser or oil control valve, low oil pressure, or issues within the engine’s timing components. |
| P0102 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Low Input | Indicates a problem with the MAF sensor circuit, such as a short to ground, a faulty MAF sensor, or wiring issues. |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (small leak) | Points to a minor leak in the evaporative emission control system, possibly from a loose or faulty gas cap, a damaged fuel tank, or compromised hoses. |
2.1. Common Powertrain OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected): This code indicates that the engine is experiencing random misfires across multiple cylinders.
- Possible Causes: Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Check and replace spark plugs and ignition coils, inspect fuel injectors, look for vacuum leaks, and perform a compression test.
- P0171/P0174 (System Too Lean Bank 1/Bank 2): These codes suggest that the engine is running with a lean air/fuel mixture.
- Possible Causes: Vacuum leaks, faulty MAF sensor, fuel pump issues, clogged fuel filter.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Inspect vacuum lines for leaks, test the MAF sensor, check fuel pressure, and replace the fuel filter if needed.
- P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold Bank 1): This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently.
- Possible Causes: Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Test oxygen sensors, inspect for exhaust leaks, and consider replacing the catalytic converter.
- P0700 (Transmission Control System Malfunction): This code indicates a general issue within the transmission control system.
- Possible Causes: Faulty transmission sensors, solenoids, valve body issues, low transmission fluid.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Check transmission fluid level and condition, test transmission sensors and solenoids, and consider a transmission service.
- P0401 (Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected): This code suggests that the EGR system is not functioning correctly.
- Possible Causes: Clogged EGR valve or passages, faulty EGR valve, vacuum leaks.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Clean or replace the EGR valve, inspect vacuum lines, and check EGR passages for clogs.
2.2. How to Diagnose Powertrain OBD2 Codes?
Diagnosing powertrain OBD2 codes involves a systematic approach:
- Read the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the specific code.
- Research the Code: Understand the code’s meaning and potential causes.
- Inspect the Vehicle: Visually inspect the related components for damage or leaks.
- Test Components: Use diagnostic tools to test sensors, actuators, and other components.
- Repair or Replace: Repair or replace faulty components as needed.
- Clear the Code: Clear the code and retest to ensure the issue is resolved.
2.3. Why is Accurate Diagnosis Important?
Accurate diagnosis is critical to avoid unnecessary repairs and ensure the problem is resolved correctly. Replacing a functioning component based on a misdiagnosis can be costly and ineffective. A systematic approach, combined with reliable information, can lead to a successful diagnosis and repair.
2.4. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help You Diagnose Powertrain OBD2 Codes?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides resources to help you accurately diagnose powertrain OBD2 codes on your Mercedes-Benz:
- Code-Specific Guides: Detailed guides for common Mercedes-Benz powertrain OBD2 codes.
- Diagnostic Tool Recommendations: Advice on selecting the best diagnostic tools for your vehicle.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Step-by-step troubleshooting tips for common issues.
- Expert Support: Access to experts who can answer your diagnostic questions.
By leveraging these resources, you can confidently diagnose and address powertrain OBD2 codes on your Mercedes-Benz.
 Mercedes diagnostic tool
Mercedes diagnostic tool
3. Diagnostic Tools for Powertrain OBD2: Choosing the Right Equipment
What diagnostic tools are best suited for reading and interpreting powertrain OBD2 codes? Selecting the right diagnostic tools can significantly impact your ability to accurately diagnose and repair powertrain issues. Here’s an overview of the essential tools and their features:
| Tool | Description | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic OBD2 Scanner | Reads and clears OBD2 codes | Reads generic OBD2 codes, displays code descriptions | Affordable, easy to use, good for basic diagnostics |
| Enhanced OBD2 Scanner | Reads and clears OBD2 codes, provides live data | Reads generic and manufacturer-specific codes, displays live sensor data, performs basic tests | Provides more detailed information, allows monitoring of vehicle performance |
| Professional Scan Tool | Advanced diagnostic capabilities | Reads all OBD2 codes, performs advanced tests (e.g., ABS, SRS), bi-directional control, programming capabilities | Comprehensive diagnostics, advanced troubleshooting, suitable for professional mechanics |
| Multimeter | Measures voltage, current, and resistance | Tests electrical circuits, sensors, and components | Essential for diagnosing electrical issues, verifying sensor functionality |
| Fuel Pressure Tester | Measures fuel pressure | Checks fuel pump performance, identifies fuel delivery issues | Helps diagnose fuel-related codes (e.g., P0171, P0174) |
| Compression Tester | Measures cylinder compression | Diagnoses low compression issues, identifies cylinder problems | Helps diagnose misfire codes (e.g., P0300, P0301) |
| Smoke Machine | Detects vacuum leaks | Identifies vacuum leaks in intake and exhaust systems | Essential for diagnosing lean codes (e.g., P0171, P0174), misfire codes |
| Oscilloscope | Displays electrical signals over time | Analyzes sensor signals, identifies intermittent electrical issues | Advanced diagnostics, useful for troubleshooting complex electrical problems |
| Diagnostic Software (e.g., | Provides in-depth diagnostics and programming capabilities for specific vehicle manufacturers (e.g., | Reads all OBD2 codes, performs advanced tests (e.g., ABS, SRS), bi-directional control, programming capabilities, access to vehicle-specific | Comprehensive diagnostics, advanced troubleshooting, suitable for professional mechanics and advanced DIYers |
| XENTRY for Mercedes-Benz) | Mercedes-Benz) | information | |
| Inspection Camera | Provides visual access to hard-to-reach areas | Allows visual inspection of engine cylinders, fuel tanks, and other components | Useful for identifying physical damage, carbon buildup, or other issues that may not be apparent through other diagnostic methods |
3.1. Essential Diagnostic Tools for Powertrain OBD2
- OBD2 Scanner: This is the most basic tool for reading and clearing OBD2 codes. Basic scanners read generic codes, while enhanced scanners read manufacturer-specific codes and provide live data.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is essential for testing electrical circuits, sensors, and components.
- Fuel Pressure Tester: This tool measures fuel pressure, helping diagnose fuel delivery issues.
- Compression Tester: A compression tester measures cylinder compression, helping diagnose misfire codes.
- Smoke Machine: A smoke machine detects vacuum leaks, which can cause lean codes and misfires.
3.2. Advanced Diagnostic Tools for Powertrain OBD2
- Professional Scan Tool: These tools offer advanced diagnostic capabilities, such as bi-directional control, ABS/SRS diagnostics, and programming capabilities.
- Oscilloscope: An oscilloscope displays electrical signals over time, useful for analyzing sensor signals and identifying intermittent electrical issues.
- Diagnostic Software: Software like XENTRY (for Mercedes-Benz) provides in-depth diagnostics and programming capabilities.
- Inspection Camera: This tool allows visual inspection of hard-to-reach areas, such as engine cylinders and fuel tanks.
3.3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
When selecting an OBD2 scanner, consider the following factors:
- Code Coverage: Does the scanner read generic and manufacturer-specific codes?
- Live Data: Does the scanner display live sensor data?
- Ease of Use: Is the scanner easy to use and navigate?
- Features: Does the scanner offer advanced features like bi-directional control or ABS/SRS diagnostics?
- Price: How does the scanner fit within your budget?
3.4. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help You Choose the Right Tools?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert advice on selecting the best diagnostic tools for your Mercedes-Benz:
- Tool Reviews: Unbiased reviews of OBD2 scanners and other diagnostic tools.
- Comparison Guides: Comparison guides to help you choose the right tool for your needs.
- Expert Recommendations: Recommendations from experienced Mercedes-Benz technicians.
- Where to Buy: Links to reputable retailers where you can purchase diagnostic tools.
By leveraging these resources, you can confidently select the right diagnostic tools for your Mercedes-Benz and effectively diagnose powertrain OBD2 codes.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Powertrain OBD2 Codes
How do you systematically diagnose powertrain OBD2 codes? A systematic approach to diagnosing powertrain OBD2 codes ensures accurate identification of the root cause and effective resolution. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
| Step | Action | Description | Tools Needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Read the OBD2 Code | Connect an OBD2 scanner to the vehicle’s OBD2 port and read the stored codes. | OBD2 Scanner |
| 2 | Record the Code and Freeze Frame Data | Record the code and any freeze frame data (snapshot of sensor readings at the time the code was triggered). | OBD2 Scanner |
| 3 | Research the Code | Research the code’s meaning and potential causes using online resources, repair manuals, or diagnostic software. | Internet Access, Repair Manual, Diagnostic Software |
| 4 | Visual Inspection | Visually inspect the related components for damage, leaks, or loose connections. | Flashlight, Inspection Mirror |
| 5 | Component Testing | Test the related sensors, actuators, and other components using a multimeter, fuel pressure tester, compression tester, or other diagnostic tools. | Multimeter, Fuel Pressure Tester, Compression Tester, Other Diagnostic Tools |
| 6 | Wiring Inspection | Inspect the wiring and connectors for damage, corrosion, or loose connections. | Multimeter, Wiring Diagram |
| 7 | Vacuum Leak Test | Perform a vacuum leak test using a smoke machine or carburetor cleaner. | Smoke Machine or Carburetor Cleaner |
| 8 | Data Analysis | Analyze live sensor data to identify any abnormal readings or patterns. | OBD2 Scanner with Live Data, Diagnostic Software |
| 9 | Repair or Replace Components | Repair or replace faulty components as needed. | Appropriate Tools and Replacement Parts |
| 10 | Clear the Code and Retest | Clear the code and retest to ensure the issue is resolved. | OBD2 Scanner |
4.1. Step 1: Read the OBD2 Code
Connect an OBD2 scanner to the vehicle’s OBD2 port and read the stored codes. Record the code and any freeze frame data (a snapshot of sensor readings at the time the code was triggered).
4.2. Step 2: Research the Code
Research the code’s meaning and potential causes using online resources, repair manuals, or diagnostic software. Understanding the code’s definition and possible causes is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
4.3. Step 3: Visual Inspection
Visually inspect the related components for damage, leaks, or loose connections. Look for obvious signs of damage, such as cracked hoses, damaged wiring, or leaking fluids.
4.4. Step 4: Component Testing
Test the related sensors, actuators, and other components using a multimeter, fuel pressure tester, compression tester, or other diagnostic tools. Component testing helps verify the functionality of individual components and narrow down the possible causes.
4.5. Step 5: Wiring Inspection
Inspect the wiring and connectors for damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Wiring issues can often cause sensor malfunctions or intermittent problems.
4.6. Step 6: Vacuum Leak Test
Perform a vacuum leak test using a smoke machine or carburetor cleaner. Vacuum leaks can cause lean codes and misfires.
4.7. Step 7: Data Analysis
Analyze live sensor data to identify any abnormal readings or patterns. Live data analysis can provide valuable insights into the performance of various systems and components.
4.8. Step 8: Repair or Replace Components
Repair or replace faulty components as needed. Ensure that you use high-quality replacement parts that meet or exceed the manufacturer’s specifications.
4.9. Step 9: Clear the Code and Retest
Clear the code and retest to ensure the issue is resolved. After completing the repairs, clear the code and perform a test drive to ensure that the issue is resolved and the code does not return.
4.10. Why is Following a Systematic Approach Important?
Following a systematic approach ensures that you address all potential causes and avoid overlooking critical details. This can save time and money by preventing unnecessary repairs and ensuring the problem is resolved correctly the first time.
4.11. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help You with Diagnostics?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides resources to guide you through the diagnostic process:
- Detailed Guides: Step-by-step diagnostic guides for common Mercedes-Benz powertrain OBD2 codes.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Expert troubleshooting tips for common issues.
- Wiring Diagrams: Access to wiring diagrams for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Community Support: Access to a community of Mercedes-Benz enthusiasts and experts who can provide assistance.
By leveraging these resources, you can confidently diagnose and address powertrain OBD2 codes on your Mercedes-Benz.
5. Repairing Powertrain Issues: Common Fixes and Procedures
What are some common repairs for powertrain OBD2 issues, and how are they performed? Addressing powertrain OBD2 codes often involves specific repairs or component replacements. Here are some common fixes and procedures:
| Code | Issue | Common Fixes |
|---|---|---|
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire | Replace faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors. Check for vacuum leaks and repair as needed. Perform a compression test and address any low compression issues. |
| P0171/ | System Too Lean | Inspect and repair vacuum leaks. Clean or replace the MAF sensor. Check fuel pressure and replace the fuel filter if needed. Inspect and clean or replace fuel injectors. |
| P0174 | ||
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below | Test oxygen sensors and replace if faulty. Inspect for exhaust leaks and repair as needed. Consider replacing the catalytic converter. |
| Threshold | ||
| P0700 | Transmission Control System Malfunction | Check transmission fluid level and condition. Test transmission sensors and solenoids and replace if faulty. Consider a transmission service or rebuild. |
| P0401 | EGR Flow Insufficient | Clean or replace the EGR valve. Inspect vacuum lines and repair as needed. Check EGR passages for clogs and clean as needed. |
| P0101 | MAF Sensor Range/Performance | Clean or replace the MAF sensor. Inspect for vacuum leaks and repair as needed. Check for intake restrictions and remove as needed. |
| P0113 | IAT Sensor Circuit High | Replace the IAT sensor. Inspect wiring and connectors and repair as needed. |
| P0011/ | Camshaft Position Timing Over-Advanced | Inspect and replace the camshaft position sensor. Check the oil control valve for proper operation. Verify proper oil pressure. Inspect the timing chain for wear or damage. |
| P0014 | ||
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System | Start by tightening or replacing the gas cap to ensure a proper seal. If the issue persists, inspect hoses, fuel tank, and other components of the evaporative emission control system for leaks or damage. Consider using a smoke test to locate the source of the leak. |
| Leak Detected |
5.1. Common Powertrain Repairs
- Replacing Spark Plugs: Spark plugs are essential for igniting the air/fuel mixture in the engine. Over time, they can become worn or fouled, causing misfires. Replacing spark plugs is a relatively simple procedure that can improve engine performance and fuel economy.
- Replacing Ignition Coils: Ignition coils provide the high-voltage spark needed to ignite the air/fuel mixture. Faulty ignition coils can cause misfires and poor engine performance. Replacing ignition coils is a straightforward procedure that can resolve misfire issues.
- Cleaning or Replacing the MAF Sensor: The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. A dirty or faulty MAF sensor can cause lean codes and poor engine performance. Cleaning or replacing the MAF sensor can resolve these issues.
- Replacing Oxygen Sensors: Oxygen sensors monitor the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. Faulty oxygen sensors can cause incorrect air/fuel ratios and emissions problems. Replacing oxygen sensors is a common repair that can improve fuel economy and emissions.
- Cleaning or Replacing the EGR Valve: The EGR valve recirculates exhaust gases back into the engine to reduce emissions. A clogged or faulty EGR valve can cause EGR flow issues. Cleaning or replacing the EGR valve can resolve these issues.
5.2. Step-by-Step Repair Procedures
- Replacing Spark Plugs:
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Remove the ignition coils.
- Remove the spark plugs using a spark plug socket.
- Install the new spark plugs, tightening them to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
- Reinstall the ignition coils.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Replacing Ignition Coils:
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the ignition coil.
- Remove the ignition coil mounting bolts.
- Remove the ignition coil.
- Install the new ignition coil and mounting bolts.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Cleaning the MAF Sensor:
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the MAF sensor.
- Remove the MAF sensor from the air intake tube.
- Spray the MAF sensor with MAF sensor cleaner.
- Allow the MAF sensor to dry completely.
- Reinstall the MAF sensor.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
5.3. Why is Proper Repair Important?
Proper repair is essential to ensure that the issue is resolved correctly and does not cause further damage. Using high-quality replacement parts and following the manufacturer’s recommended procedures can ensure a successful repair.
5.4. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help You with Repairs?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides resources to guide you through the repair process:
- Repair Manuals: Access to repair manuals for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Step-by-Step Guides: Step-by-step repair guides for common issues.
- Video Tutorials: Video tutorials demonstrating common repair procedures.
- Community Support: Access to a community of Mercedes-Benz enthusiasts and experts who can provide assistance.
By leveraging these resources, you can confidently perform repairs on your Mercedes-Benz and address powertrain OBD2 codes.
6. Preventing Powertrain OBD2 Codes: Maintenance and Best Practices
How can regular maintenance and best practices help prevent powertrain OBD2 codes? Preventing powertrain OBD2 codes through regular maintenance and best practices can save time, money, and hassle. Here are some essential maintenance tasks and best practices:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Changes | Every 5,000-7,500 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer | Keeps the engine lubricated, reduces wear, and prevents sludge buildup. |
| Air Filter Replacement | Every 12,000-15,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer | Ensures proper airflow to the engine, improving performance and fuel economy. |
| Spark Plug Replacement | Every 30,000-50,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer | Ensures proper ignition, preventing misfires and improving engine performance. |
| Fuel Filter Replacement | Every 30,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer | Ensures clean fuel delivery to the engine, preventing fuel system issues and improving performance. |
| Transmission Fluid Change | Every 30,000-60,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer | Keeps the transmission lubricated, preventing wear and ensuring smooth shifting. |
| Coolant Flush | Every 24,000-36,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer | Prevents corrosion and overheating, ensuring proper engine cooling. |
| Regular Inspections | Every 6 months or as needed | Identifies potential issues early on, allowing for timely repairs and preventing more significant problems. |
| Use High-Quality Fuel and Fluids | Always | Ensures proper engine and transmission performance and prevents premature wear. |
| Avoid Harsh Driving Conditions | Whenever possible | Reduces stress on the engine and transmission, preventing premature wear and potential issues. |
| Address Issues Promptly | As soon as they are detected | Prevents minor issues from escalating into more significant problems. |
| Monitor Vehicle Performance | Regularly | Helps identify potential issues early on, allowing for timely repairs and preventing more significant problems. |
| Keep Vehicle Clean | Regularly | Prevents corrosion and damage to components, ensuring proper performance. |
| Follow Manufacturer Recommendations | Always | Ensures that maintenance tasks are performed at the proper intervals and using the correct procedures. |
| Check and Maintain Tires | Regularly | Proper tire inflation and condition contribute to overall vehicle performance and safety, and can impact fuel efficiency and drivetrain health. |
6.1. Essential Maintenance Tasks
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes are essential for keeping the engine lubricated and preventing wear. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals and use high-quality oil.
- Air Filter Replacement: A clean air filter ensures proper airflow to the engine, improving performance and fuel economy. Replace the air filter as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Spark plugs ensure proper ignition, preventing misfires and improving engine performance. Replace the spark plugs as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Fuel Filter Replacement: A clean fuel filter ensures clean fuel delivery to the engine, preventing fuel system issues and improving performance. Replace the fuel filter as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Transmission Fluid Change: Regular transmission fluid changes keep the transmission lubricated, preventing wear and ensuring smooth shifting. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended transmission fluid change intervals.
6.2. Best Practices
- Use High-Quality Fuel and Fluids: Using high-quality fuel and fluids ensures proper engine and transmission performance and prevents premature wear.
- Avoid Harsh Driving Conditions: Harsh driving conditions can put excessive stress on the engine and transmission, leading to premature wear and potential issues.
- Address Issues Promptly: Addressing issues as soon as they are detected can prevent minor problems from escalating into more significant issues.
- Monitor Vehicle Performance: Regularly monitoring vehicle performance can help identify potential issues early on, allowing for timely repairs and preventing more significant problems.
- Follow Manufacturer Recommendations: Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance tasks and procedures ensures that the vehicle is properly maintained and potential issues are addressed.
6.3. Why is Preventative Maintenance Important?
Preventative maintenance is essential for maintaining the long-term health and reliability of your vehicle. By performing regular maintenance tasks and following best practices, you can prevent powertrain OBD2 codes and ensure that your vehicle operates smoothly and efficiently.
6.4. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help You with Preventative Maintenance?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides resources to help you with preventative maintenance:
- Maintenance Schedules: Access to maintenance schedules for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Maintenance Guides: Step-by-step maintenance guides for common tasks.
- Product Recommendations: Recommendations for high-quality fuel, fluids, and replacement parts.
- Community Support: Access to a community of Mercedes-Benz enthusiasts and experts who can provide assistance.
By leveraging these resources, you can confidently perform preventative maintenance on your Mercedes-Benz and prevent powertrain OBD2 codes.
7. Advanced Powertrain Diagnostics: Going Beyond the Basics
When do you need advanced powertrain diagnostics, and what does it entail? While basic OBD2 diagnostics can address many powertrain issues, some situations require advanced diagnostic techniques. Here’s an overview of advanced diagnostics and when they are needed:
| Scenario | Advanced Diagnostic Techniques |
|---|---|
| Intermittent Issues | Using an oscilloscope to capture intermittent sensor signals, performing wiggle tests on wiring harnesses, and using data logging to monitor system performance over time. |
| Complex System Interactions | Analyzing data from multiple sensors and systems to identify interactions and dependencies, using advanced diagnostic software to perform system tests, and consulting with experienced technicians. |
| Lack of DTCs | Performing manual tests on individual components, using a compression tester to check cylinder compression, and using a smoke machine to check for vacuum leaks. |
| Unclear Code Definitions | Consulting with experienced technicians, using manufacturer-specific diagnostic software, and researching code definitions in repair manuals. |
| Driveability Problems | Analyzing live sensor data during a test drive, performing road tests to simulate real-world driving conditions, and using advanced diagnostic software to monitor system performance. |
| Aftermarket Modifications | Inspecting aftermarket modifications for compatibility issues, consulting with experienced technicians, and using advanced diagnostic software to reprogram the vehicle’s computer. |
| Repeated Failures | Analyzing the root cause of the failure, inspecting related components for damage, and using advanced diagnostic software to perform system tests. |
| Performance Tuning and Optimization | Using advanced diagnostic software to monitor system performance, making adjustments to engine parameters, and performing dyno tests to measure performance improvements. |
| Emissions Testing Failures | Analyzing exhaust gas composition, inspecting emissions control components, and using advanced diagnostic software to perform emissions system tests. |
| Undetectable Problems with Standard OBD2 Tools | Utilizing specialized diagnostic equipment, such as NVH (Noise, Vibration, and Harshness) analyzers, to pinpoint issues that don’t trigger standard OBD2 codes. |
7.1. When Are Advanced Diagnostics Needed?
- Intermittent Issues: When the problem is not consistently present, advanced diagnostics are needed to capture the issue when it occurs.
- Complex System Interactions: When the problem involves multiple systems interacting with each other, advanced diagnostics are needed to analyze the interactions and identify the root cause.
- Lack of DTCs: When there are driveability problems but no DTCs, advanced diagnostics are needed to identify the underlying issue.
- Unclear Code Definitions: When the code definition is unclear or does not provide enough information, advanced diagnostics are