The Chevrolet OBD2 protocol is a standardized system crucial for diagnosing vehicle issues, and at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide in-depth knowledge and tools to master it. Understanding this protocol empowers you to identify problems, maintain your vehicle efficiently, and unlock hidden features. Dive into the intricacies of OBD-II, including its purpose, implementation across Chevrolet models, and the benefits of utilizing MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for optimal vehicle performance.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 Protocols
- 1.1. What is OBD2?
- 1.2. Why Was OBD2 Introduced?
- 1.3. Key Functions of OBD2
- 1.4. The Significance of Standardization
- 2. Understanding OBD2 Protocols for Chevrolet Vehicles
- 2.1. Overview of OBD2 Protocols
- 2.2. Which Protocols Do Chevrolet Vehicles Use?
- 2.3. Identifying the Protocol in Your Chevrolet
- 2.4. Pin Configuration and Protocol Determination
- 2.5. Implications for Diagnostic Tools
- 3. The OBD2 Port in Chevrolet Vehicles
- 3.1. Location of the OBD2 Port
- 3.2. Identifying the OBD2 Port
- 3.3. Different Types of OBD2 Ports
- 3.4. Common Issues with the OBD2 Port
- 3.5. Troubleshooting OBD2 Port Issues
- 3.6. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 4. Reading and Interpreting OBD2 Codes on a Chevrolet
- 4.1. Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 4.2. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.3. Common OBD2 Codes in Chevrolet Vehicles
- 4.4. Interpreting the Codes
- 4.5. Clearing OBD2 Codes
- 4.6. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Helps
- 5. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures for Chevrolet
- 5.1. Live Data Monitoring
- 5.2. Freeze Frame Data
- 5.3. Actuator Tests
- 5.4. Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- 5.5. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedures
- 5.6. The Expertise of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 6. Common Chevrolet Problems Diagnosed Through OBD2
- 6.1. Engine Misfires
- 6.2. Oxygen Sensor Issues
- 6.3. Catalytic Converter Problems
- 6.4. Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) Leaks
- 6.5. Transmission Problems
- 6.6. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Assist
- 7. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Chevrolet
- 7.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners
- 7.2. Advanced OBD2 Scanners
- 7.3. Considerations When Choosing a Scanner
- 7.4. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Chevrolet
- 7.5. Why Choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 8. Maintaining Your Chevrolet with OBD2 Diagnostics
- 8.1. Regular OBD2 Scans
- 8.2. Preventive Maintenance
- 8.3. Addressing Issues Promptly
- 8.4. Benefits of Proactive Maintenance
- 8.5. Utilizing MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Maintenance
- 9. Safety Precautions When Working with OBD2 Systems
- 9.1. Disconnecting the Battery
- 9.2. Working in a Well-Ventilated Area
- 9.3. Wearing Protective Gear
- 9.4. Using the Right Tools
- 9.5. Following Repair Manuals
- 9.6. Disposing of Hazardous Waste Properly
- 9.7. The Safety Commitment of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 10. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
- 10.1. Enhanced Diagnostics
- 10.2. Integration with Telematics Systems
- 10.3. Cybersecurity
- 10.4. Standardization
- 10.5. The Innovation at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- FAQ: Unlocking the Secrets of Chevrolet OBD2 Protocols
1. Understanding the Basics of OBD2 Protocols
1.1. What is OBD2?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system implemented in all cars and light trucks sold in the United States after 1996. This system is designed to monitor the performance of a vehicle’s engine, emissions systems, and other critical components. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was mandated to ensure vehicles meet stringent emission standards, thereby contributing to cleaner air.
1.2. Why Was OBD2 Introduced?
The introduction of OBD2 was primarily driven by environmental concerns. Before OBD2, on-board diagnostic systems were manufacturer-specific, making it difficult to obtain consistent and reliable diagnostic information. The EPA mandated OBD2 to standardize diagnostic procedures, making it easier for technicians and vehicle owners to identify and address emission-related issues. This standardization also facilitates compliance with environmental regulations.
1.3. Key Functions of OBD2
OBD2 performs several key functions, including:
- Monitoring Emissions: Ensuring that the vehicle meets emission standards by monitoring components such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system.
- Detecting Malfunctions: Identifying malfunctions in the engine and related systems, alerting the driver through the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), commonly known as the “check engine” light.
- Storing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Recording specific codes that correspond to detected malfunctions, providing technicians with valuable information for diagnosing the issue.
- Providing Real-Time Data: Offering access to real-time data from various sensors and components, allowing technicians to monitor vehicle performance under different conditions.
1.4. The Significance of Standardization
The standardization of OBD2 is significant because it ensures that any compliant diagnostic tool can communicate with any OBD2-compliant vehicle, regardless of the manufacturer. This standardization has several benefits:
- Ease of Use: Technicians can use a single tool to diagnose a wide range of vehicles, saving time and reducing the need for multiple diagnostic devices.
- Cost Savings: Vehicle owners can use aftermarket OBD2 scanners to diagnose issues themselves, potentially saving money on diagnostic fees at a repair shop.
- Improved Repair Accuracy: The standardized DTCs and real-time data provide technicians with more accurate information, leading to more effective repairs.
- Environmental Protection: By ensuring that vehicles meet emission standards, OBD2 helps to reduce air pollution and protect the environment.
2. Understanding OBD2 Protocols for Chevrolet Vehicles
2.1. Overview of OBD2 Protocols
OBD2 protocols are the communication languages used by a vehicle’s computer to transmit diagnostic information. There are five primary OBD2 protocols:
- J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily by Ford vehicles.
- J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Used primarily by General Motors (GM) vehicles.
- ISO9141-2: Used by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO14230-4 (Keyword Protocol 2000): Also used by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO15765-4/SAE J2480 (CAN – Controller Area Network): The modern standard, used by all vehicles sold in the US since 2008.
2.2. Which Protocols Do Chevrolet Vehicles Use?
Chevrolet vehicles have used different OBD2 protocols over the years:
- Early Models (Pre-2003): Primarily used J1850 VPW. This protocol was common in GM vehicles during the early years of OBD2 implementation.
- Transitional Models (2003-2007): Some Chevrolet vehicles during this period may have used a combination of J1850 VPW and ISO15765-4 (CAN).
- Modern Models (2008 and Newer): All Chevrolet vehicles now use ISO15765-4 (CAN). This protocol offers faster communication speeds and more advanced diagnostic capabilities.
2.3. Identifying the Protocol in Your Chevrolet
To determine the specific OBD2 protocol used in your Chevrolet, you can:
- Check the Vehicle’s OBD2 Port: Examine the pins in the OBD2 port (also known as the Diagnostic Link Connector or DLC). The presence of specific pins indicates the protocol used.
- Consult the Vehicle’s Repair Manual: The repair manual provides detailed information about the vehicle’s systems, including the OBD2 protocol.
- Use an OBD2 Scanner: Some advanced OBD2 scanners can automatically detect the protocol used by the vehicle.
2.4. Pin Configuration and Protocol Determination
The pin configuration of the OBD2 port can help you identify the protocol:
- J1850 VPW: Pin 2 should be populated.
- ISO9141-2 or ISO14230-4: Pin 7 should be populated.
- ISO15765-4 (CAN): Pins 6 and 14 should be populated.
In addition to these, the connector should always have pins 4 (Chassis Ground), 5 (Signal Ground), and 16 (Battery Positive).
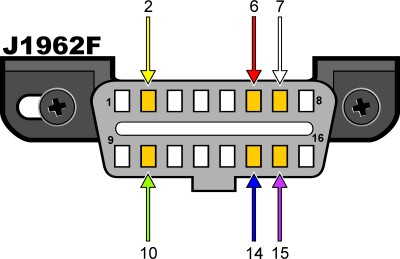 J1962F OBDII connector pinout
J1962F OBDII connector pinout
Figure 3: OBDII Connector Pinout
2.5. Implications for Diagnostic Tools
Knowing the correct OBD2 protocol is crucial when selecting a diagnostic tool. Using a tool that is not compatible with the vehicle’s protocol can result in communication errors or inaccurate diagnostic information. At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we ensure that our diagnostic tools are compatible with all OBD2 protocols used by Chevrolet vehicles, providing reliable and accurate diagnostics.
3. The OBD2 Port in Chevrolet Vehicles
3.1. Location of the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port, also known as the Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC), is a standardized 16-pin connector used to access the vehicle’s diagnostic information. According to SAE J1962 standards, the OBD2 port must be located in the passenger compartment. In Chevrolet vehicles, the OBD2 port is typically found:
- Under the dashboard on the driver’s side
- Near the center console
- Inside the glove box (less common)
3.2. Identifying the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is usually trapezoidal and has 16 pins. It is designed to be easily accessible, allowing technicians and vehicle owners to connect diagnostic tools quickly.
3.3. Different Types of OBD2 Ports
There are two types of OBD2 ports defined by SAE J1962:
- Type A: This is the most common type and is typically found in passenger vehicles.
- Type B: This type is less common and is often used in heavy-duty vehicles.
The main difference between the two types is the shape of the alignment tab.
 J1962F, Type A
J1962F, Type A
Figure 1 – J1962 Vehicle Connector, Type A
 J1962F, Type B
J1962F, Type B
Figure 2 – J1962 Vehicle Connector, Type B
3.4. Common Issues with the OBD2 Port
Several issues can affect the OBD2 port, including:
- Physical Damage: The port can be damaged due to accidental impacts or improper use of diagnostic tools.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture and environmental elements can cause corrosion on the pins, leading to poor connectivity.
- Loose Connections: The pins may become loose over time, resulting in intermittent or no communication with the diagnostic tool.
- Wiring Issues: Problems with the wiring connected to the OBD2 port can also prevent proper communication.
3.5. Troubleshooting OBD2 Port Issues
If you encounter issues with the OBD2 port, you can try the following troubleshooting steps:
- Inspect the Port: Check for any visible damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Clean the Pins: Use a contact cleaner to remove any corrosion or debris from the pins.
- Check the Wiring: Ensure that the wiring connected to the port is intact and properly connected.
- Test with Another Tool: Try connecting a different diagnostic tool to see if the issue is with the port or the tool.
3.6. The Role of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive support for diagnosing and resolving OBD2 port issues. Our diagnostic tools are designed to work seamlessly with Chevrolet vehicles, and our expert technicians can provide guidance on troubleshooting any problems you may encounter.
4. Reading and Interpreting OBD2 Codes on a Chevrolet
4.1. Using an OBD2 Scanner
To read OBD2 codes on a Chevrolet, you need an OBD2 scanner. Here’s how to use it:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port in your Chevrolet, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: The scanner should power on automatically. If not, ensure it has batteries or is properly connected.
- Read the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
4.2. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs are five-character codes that identify specific issues detected by the OBD2 system. These codes are standardized across all OBD2-compliant vehicles, making it easier to diagnose problems. A typical DTC consists of a letter followed by four numbers:
- First Character: Indicates the system related to the code:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (interior, exterior)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension)
- U: Network (communication)
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (SAE) code
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code
- Third Character: Indicates the specific subsystem:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed control, idle control system
- 6: Computer output circuit
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specify the specific fault within the subsystem.
4.3. Common OBD2 Codes in Chevrolet Vehicles
Some common OBD2 codes found in Chevrolet vehicles include:
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1) – Indicates that the engine is running with too little fuel or too much air.
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected – Indicates that the engine is experiencing misfires in one or more cylinders.
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) – Indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently.
- P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) – Indicates a small leak in the evaporative emission control system.
- P0455: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Gross Leak) – Indicates a large leak in the evaporative emission control system.
4.4. Interpreting the Codes
Once you have retrieved the DTCs, you need to interpret them to understand the underlying issue. Here’s how:
- Consult the Vehicle’s Repair Manual: The repair manual provides detailed descriptions of each DTC, along with possible causes and troubleshooting steps.
- Use Online Resources: Websites like OBD-Codes.com offer extensive databases of DTCs and their meanings.
- Consult a Professional: If you are unsure about the meaning of a code or how to proceed with repairs, consult a qualified mechanic.
4.5. Clearing OBD2 Codes
After addressing the underlying issue, you can clear the OBD2 codes using the scanner. Here’s how:
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Clear the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to clear the stored DTCs.
Note: Clearing the codes does not fix the underlying issue. It only resets the system. If the problem persists, the code will reappear.
4.6. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Helps
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed resources and expert support to help you read, interpret, and clear OBD2 codes on your Chevrolet. Our advanced diagnostic tools offer features like code definitions, possible causes, and troubleshooting tips, making it easier to diagnose and resolve vehicle issues.
5. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures for Chevrolet
5.1. Live Data Monitoring
Live data monitoring involves observing real-time data from various sensors and components in the vehicle. This allows technicians to diagnose issues by monitoring how the engine and related systems are performing under different conditions. Key parameters to monitor include:
- Engine RPM: Revolutions per minute of the engine.
- Vehicle Speed: Speed of the vehicle in miles per hour (mph) or kilometers per hour (km/h).
- Engine Load: Percentage of maximum engine power being used.
- Coolant Temperature: Temperature of the engine coolant.
- Intake Air Temperature: Temperature of the air entering the engine.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Voltage readings from the oxygen sensors, indicating the air-fuel ratio.
- Fuel Trim: Adjustments made by the engine control unit (ECU) to the fuel delivery.
5.2. Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the sensor values at the moment a DTC is triggered. This information can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues or conditions that are difficult to replicate. Freeze frame data typically includes:
- DTC: The diagnostic trouble code that triggered the freeze frame.
- Engine RPM: Engine speed at the time the code was triggered.
- Engine Load: Engine load at the time the code was triggered.
- Coolant Temperature: Coolant temperature at the time the code was triggered.
- Fuel Trim: Fuel trim values at the time the code was triggered.
5.3. Actuator Tests
Actuator tests involve using the diagnostic tool to activate or deactivate specific components in the vehicle to test their functionality. Common actuator tests include:
- Fuel Injector Test: Activating and deactivating the fuel injectors to test their performance.
- EGR Valve Test: Opening and closing the EGR valve to verify its operation.
- Throttle Control Test: Controlling the throttle position to test the throttle control system.
- Cooling Fan Test: Activating and deactivating the cooling fans to test their operation.
5.4. Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Advanced diagnostic tools offer features beyond basic code reading and clearing. These tools often include:
- Oscilloscope: Used to analyze electrical signals and waveforms.
- Multimeter: Used to measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Smoke Machine: Used to detect leaks in the intake or exhaust system.
- Compression Tester: Used to measure the compression in each cylinder.
5.5. Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedures
When performing advanced diagnostics on a Chevrolet, follow these steps:
- Verify the Complaint: Confirm the issue reported by the vehicle owner.
- Gather Information: Collect information about the vehicle, including its make, model, year, and engine type.
- Read DTCs: Use an OBD2 scanner to read any stored diagnostic trouble codes.
- Research DTCs: Consult the vehicle’s repair manual or online resources to understand the meaning of the codes.
- Check Freeze Frame Data: Analyze the freeze frame data to identify the conditions that triggered the code.
- Perform Visual Inspection: Inspect the engine and related systems for any obvious signs of damage or wear.
- Monitor Live Data: Use the diagnostic tool to monitor live data from various sensors and components.
- Perform Actuator Tests: Use the diagnostic tool to activate or deactivate specific components to test their functionality.
- Perform Component Tests: Use an oscilloscope, multimeter, or other tools to test the individual components.
- Repair or Replace Faulty Components: Repair or replace any components that are found to be faulty.
- Clear DTCs: Clear the DTCs after addressing the underlying issue.
- Verify the Repair: Test the vehicle to ensure that the issue has been resolved.
5.6. The Expertise of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer a wide range of advanced diagnostic tools and comprehensive training programs to help you master advanced diagnostic procedures for Chevrolet vehicles. Our expert technicians can provide guidance and support to help you diagnose and resolve even the most challenging issues.
6. Common Chevrolet Problems Diagnosed Through OBD2
6.1. Engine Misfires
Engine misfires are a common issue in Chevrolet vehicles, often indicated by the OBD2 code P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected). Misfires can be caused by:
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Worn or damaged spark plugs can cause incomplete combustion.
- Faulty Ignition Coils: Malfunctioning ignition coils can prevent the spark plugs from firing properly.
- Faulty Fuel Injectors: Clogged or malfunctioning fuel injectors can disrupt fuel delivery to the cylinders.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake manifold or vacuum lines can alter the air-fuel mixture.
- Low Compression: Low compression in one or more cylinders can prevent proper combustion.
6.2. Oxygen Sensor Issues
Oxygen sensor issues are also common and can trigger codes such as P0131 (O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage – Bank 1 Sensor 1) or P0171 (System Too Lean – Bank 1). These issues can be caused by:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: Oxygen sensors can fail due to age, contamination, or electrical damage.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system can affect the oxygen sensor readings.
- Vacuum Leaks: Vacuum leaks can also affect the oxygen sensor readings by altering the air-fuel mixture.
- Fuel Injector Issues: Problems with the fuel injectors can cause the engine to run lean or rich, affecting the oxygen sensor readings.
6.3. Catalytic Converter Problems
Catalytic converter problems can trigger codes such as P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold – Bank 1). These issues can be caused by:
- Damaged Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter can be damaged due to overheating, contamination, or physical damage.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system can reduce the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
- Engine Issues: Engine problems such as misfires or excessive oil consumption can damage the catalytic converter.
6.4. Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) Leaks
EVAP leaks are a common issue and can trigger codes such as P0442 (Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected – Small Leak) or P0455 (Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected – Gross Leak). These leaks can be caused by:
- Faulty Gas Cap: A loose or damaged gas cap can cause a leak in the EVAP system.
- Faulty Purge Valve: A malfunctioning purge valve can prevent the EVAP system from functioning properly.
- Cracked Hoses: Cracks or leaks in the EVAP system hoses can cause leaks.
- Faulty Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor: A malfunctioning fuel tank pressure sensor can trigger EVAP codes.
6.5. Transmission Problems
Transmission problems can trigger various OBD2 codes, depending on the specific issue. Common codes include:
- P0700: Transmission Control System Malfunction – Indicates a general issue with the transmission control system.
- P0741: Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off – Indicates a problem with the torque converter clutch.
- P0751: Shift Solenoid A Performance or Stuck Off – Indicates a problem with the shift solenoid.
6.6. How MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Assist
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed diagnostic information and troubleshooting tips for all of these common Chevrolet problems. Our expert technicians can help you interpret the OBD2 codes and perform the necessary repairs to get your vehicle back on the road.
7. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Chevrolet
7.1. Basic OBD2 Scanners
Basic OBD2 scanners are designed for reading and clearing DTCs. These scanners are typically inexpensive and easy to use, making them a good option for vehicle owners who want to perform basic diagnostics. Features of basic OBD2 scanners include:
- Code Reading: Ability to read and display DTCs.
- Code Clearing: Ability to clear stored DTCs.
- Code Definitions: Display of basic code definitions.
7.2. Advanced OBD2 Scanners
Advanced OBD2 scanners offer more features and capabilities than basic scanners. These scanners are typically used by professional technicians and experienced DIYers. Features of advanced OBD2 scanners include:
- Live Data Monitoring: Ability to monitor real-time data from various sensors and components.
- Freeze Frame Data: Ability to view freeze frame data.
- Actuator Tests: Ability to perform actuator tests.
- Enhanced Code Definitions: More detailed code definitions and troubleshooting tips.
- Bi-Directional Control: Ability to send commands to the vehicle’s computer to control specific functions.
- Software Updates: Ability to update the scanner’s software to support newer vehicles and features.
7.3. Considerations When Choosing a Scanner
When choosing an OBD2 scanner for your Chevrolet, consider the following:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the scanner is compatible with the OBD2 protocol used by your Chevrolet.
- Features: Choose a scanner with the features you need for your diagnostic tasks.
- Ease of Use: Select a scanner that is easy to use and has a clear, intuitive interface.
- Price: Set a budget and choose a scanner that offers the best value for your money.
- Reviews: Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the scanner’s performance and reliability.
7.4. Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Chevrolet
Some recommended OBD2 scanners for Chevrolet vehicles include:
- INNOVA 3100i: A basic scanner that offers code reading, code clearing, and code definitions.
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: An advanced scanner that offers live data monitoring, actuator tests, and bi-directional control.
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: A Bluetooth scanner that connects to your smartphone or tablet and offers advanced diagnostic features.
- LAUNCH CRP129E: An advanced scanner that offers live data monitoring, actuator tests, and special functions.
7.5. Why Choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer a wide selection of OBD2 scanners to meet your diagnostic needs. Our expert technicians can help you choose the right scanner for your Chevrolet and provide guidance on how to use it effectively. We ensure that our scanners are compatible with all OBD2 protocols used by Chevrolet vehicles, providing reliable and accurate diagnostics.
8. Maintaining Your Chevrolet with OBD2 Diagnostics
8.1. Regular OBD2 Scans
Performing regular OBD2 scans can help you identify potential issues before they become major problems. It is recommended to scan your Chevrolet:
- After a “Check Engine” Light: When the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) illuminates.
- Before a Long Trip: To ensure that your vehicle is in good condition for the trip.
- During Routine Maintenance: As part of your regular maintenance schedule.
- After Repairs: To verify that the repairs have been performed correctly.
8.2. Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is crucial for keeping your Chevrolet in good condition and preventing costly repairs. Regular maintenance tasks include:
- Oil Changes: Changing the engine oil and filter according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Fluid Checks: Checking and topping off all fluids, including coolant, brake fluid, power steering fluid, and transmission fluid.
- Filter Replacements: Replacing the air filter, fuel filter, and cabin air filter.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Replacing the spark plugs according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Tire Rotations: Rotating the tires to ensure even wear.
- Brake Inspections: Inspecting the brakes for wear and tear.
8.3. Addressing Issues Promptly
Addressing issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into more significant problems. If you detect a DTC, research the code and take the necessary steps to address the underlying issue. Ignoring DTCs can lead to reduced fuel economy, poor performance, and costly repairs.
8.4. Benefits of Proactive Maintenance
Proactive maintenance offers several benefits, including:
- Improved Reliability: Keeping your Chevrolet in good condition reduces the risk of breakdowns and unexpected repairs.
- Extended Vehicle Life: Regular maintenance can extend the life of your vehicle.
- Enhanced Performance: Maintaining your vehicle can improve its performance and fuel economy.
- Increased Safety: Properly maintained brakes, tires, and other safety systems can enhance your safety on the road.
- Higher Resale Value: A well-maintained vehicle typically has a higher resale value.
8.5. Utilizing MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Maintenance
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive resources and support for maintaining your Chevrolet. Our expert technicians can provide guidance on performing routine maintenance tasks, interpreting OBD2 codes, and addressing any issues you may encounter.
9. Safety Precautions When Working with OBD2 Systems
9.1. Disconnecting the Battery
When working on the electrical system of your Chevrolet, it is essential to disconnect the battery to prevent electrical shocks or damage to the vehicle’s components. Here’s how:
- Locate the Battery: Find the battery in your Chevrolet, typically located under the hood or in the trunk.
- Disconnect the Negative Terminal: Use a wrench to loosen the nut on the negative (-) battery terminal and remove the cable.
- Disconnect the Positive Terminal: Use a wrench to loosen the nut on the positive (+) battery terminal and remove the cable.
- Secure the Cables: Secure the cables to prevent them from accidentally contacting the battery terminals.
9.2. Working in a Well-Ventilated Area
When working on the engine or fuel system of your Chevrolet, it is essential to work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling harmful fumes. Open the garage door or work outside to ensure adequate ventilation.
9.3. Wearing Protective Gear
When working on your Chevrolet, it is essential to wear protective gear to prevent injuries. Protective gear includes:
- Safety Glasses: To protect your eyes from debris and chemicals.
- Gloves: To protect your hands from dirt, grease, and chemicals.
- Work Boots: To protect your feet from falling objects and sharp objects.
9.4. Using the Right Tools
Using the right tools is essential for performing repairs safely and effectively. Use high-quality tools that are designed for automotive work. Avoid using tools that are damaged or worn, as they can cause injuries.
9.5. Following Repair Manuals
Always follow the repair manual when performing repairs on your Chevrolet. The repair manual provides detailed instructions and safety precautions for each repair procedure.
9.6. Disposing of Hazardous Waste Properly
When performing repairs, you may generate hazardous waste, such as used oil, coolant, and brake fluid. Dispose of hazardous waste properly according to local regulations. Do not pour hazardous waste down the drain or into the environment.
9.7. The Safety Commitment of MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we prioritize safety and provide detailed safety guidelines for working with OBD2 systems and performing repairs on Chevrolet vehicles. Our expert technicians can provide guidance on safe repair procedures and help you avoid potential hazards.
10. Future Trends in OBD2 Technology
10.1. Enhanced Diagnostics
Future OBD2 systems are expected to offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities, including:
- More Detailed DTCs: More specific and informative diagnostic trouble codes.
- Advanced Sensor Monitoring: Enhanced monitoring of various sensors and components.
- Predictive Diagnostics: Ability to predict potential issues before they occur.
- Remote Diagnostics: Ability to perform diagnostics remotely using telematics systems.
10.2. Integration with Telematics Systems
OBD2 systems are increasingly being integrated with telematics systems, allowing vehicle owners and service providers to access diagnostic information remotely. This integration enables features such as:
- Automatic Crash Notification: Automatic notification of emergency services in the event of a crash.
- Stolen Vehicle Tracking: Ability to track a stolen vehicle.
- Remote Diagnostics: Ability to perform diagnostics remotely.
- Maintenance Reminders: Automatic maintenance reminders based on vehicle usage.
10.3. Cybersecurity
As OBD2 systems become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important. Future OBD2 systems will need to incorporate robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and protect against cyberattacks.
10.4. Standardization
Efforts are ongoing to further standardize OBD2 systems and protocols. This standardization will make it easier for technicians and vehicle owners to diagnose and repair vehicles, regardless of the manufacturer.
10.5. The Innovation at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are committed to staying at the forefront of OBD2 technology. We continuously update our diagnostic tools and training programs to incorporate the latest advancements, ensuring that our customers have access to the most advanced and effective diagnostic solutions.
FAQ: Unlocking the Secrets of Chevrolet OBD2 Protocols
1. What exactly is the Chevrolet OBD2 protocol?
The Chevrolet OBD2 protocol refers to the standardized communication methods used by Chevrolet vehicles to transmit diagnostic information via the On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system. It helps mechanics and car owners diagnose issues, monitor performance, and ensure compliance with emission standards.
2. How do I determine which OBD2 protocol my Chevrolet uses?
You can identify the OBD2 protocol by checking your vehicle’s repair manual, examining the pins in the OBD2 port, or using an advanced OBD2 scanner that automatically detects the protocol.
3. Where is the OBD2 port located in a Chevrolet vehicle?
In Chevrolet vehicles, the OBD2 port is typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the center console, or inside the glove box.
4. What are common issues I can diagnose on my Chevrolet using OBD2?
Common issues diagnosable through OBD2 include engine misfires, oxygen sensor problems, catalytic converter issues, evaporative emission control system leaks, and transmission problems.
5. Can I clear OBD2 codes myself, and how?
Yes, you can clear OBD2 codes using an OBD2 scanner. Connect the scanner, turn on the ignition without starting the engine, and follow the scanner’s instructions to clear the stored DTCs.
6. What type of OBD2 scanner should I choose for my Chevrolet?
For basic diagnostics, a simple code reader is sufficient. For more in-depth analysis, consider an advanced scanner with live data monitoring, freeze frame data, and actuator tests.
7. Is it safe to work with OBD2 systems on my Chevrolet?
Yes, but it’s crucial to take safety precautions, such as disconnecting the battery, working in a well-ventilated area, wearing protective gear, and following repair manuals.
8. What are actuator tests, and how are they useful?
Actuator tests involve using a diagnostic tool to activate or deactivate specific components to test their functionality, such as fuel injectors, EGR valves, and throttle control systems.
9. How often should I perform an OBD2 scan on my Chevrolet?
It’s recommended to scan your Chevrolet after a check engine light appears, before long trips, during routine maintenance, and after repairs.
10. Where can I find expert support for Chevrolet OBD2 diagnostics?
MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive resources, advanced diagnostic tools, and expert support to help you effectively diagnose and resolve vehicle issues using OBD2 systems.
Do you have a check engine light on in your Chevrolet and need expert assistance? Contact us today at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for all your diagnostic needs. Our experienced technicians are ready to help you diagnose and resolve any issues. Visit us at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Let MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in maintaining your Chevrolet’s optimal performance.