Understanding What Are Obd2 Codes is crucial for Mercedes-Benz owners to proactively maintain their vehicles and address potential issues. With MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can decode these messages, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for your prized vehicle through effective vehicle diagnostics. Learn to interpret these codes, understand their implications, and take the necessary steps to keep your Mercedes running smoothly by diving into a detailed vehicle health check.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 Codes
- 1.1 The Role of Onboard Diagnostics (OBD2)
- 1.2 Why OBD2 Codes Matter for Mercedes-Benz Owners
- 1.3 Common OBD2 Code Readers for Mercedes-Benz
- 2. Decoding the Structure of OBD2 Codes
- 2.1 The First Character: Identifying the System
- 2.2 The Second Character: Code Type
- 2.3 The Third Character: Affected Subsystem
- 2.4 The Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Issue
- 3. Types of OBD2 Codes
- 3.1 Powertrain (P) Codes: Engine and Transmission
- 3.2 Body (B) Codes: Interior and Exterior Systems
- 3.3 Chassis (C) Codes: Brakes, Suspension, and Steering
- 3.4 Network Communication (U) Codes: Communication Issues
- 4. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings for Mercedes-Benz
- 4.1 P0171 and P0174: System Too Lean
- 4.2 P0300, P0301, P0302: Misfire Detected
- 4.3 P0400: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Malfunction
- 4.4 P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
- 4.5 B1001: Control Module Faulty
- 5. Using an OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 5.1 Locating the OBD2 Port in Your Mercedes-Benz
- 5.2 Connecting the Scanner and Reading Codes
- 5.3 Interpreting the Codes and Taking Action
- 6. Clearing OBD2 Codes: When and How
- 6.1 The Importance of Addressing the Underlying Issue
- 6.2 Step-by-Step Guide to Clearing Codes with a Scanner
- 6.3 Potential Consequences of Clearing Codes Prematurely
- 7. Preventing OBD2 Codes: Proactive Maintenance
- 7.1 The Role of Regular Maintenance
- 7.2 Using Quality Fuel and Fluids
- 7.3 Addressing Minor Issues Promptly
- 8. OBD2 Codes and Mercedes-Benz: Specific Considerations
- 8.1 Manufacturer-Specific Codes: What You Need to Know
- 8.2 Resources for Mercedes-Benz Specific Codes
- 8.3 Common Mercedes-Benz Specific Issues and Codes
- 9. Advanced Diagnostics: When to Seek Professional Help
- 9.1 Recognizing the Limits of DIY Diagnostics
- 9.2 Signs That Indicate Professional Assistance is Needed
- 9.3 Finding a Qualified Mercedes-Benz Mechanic
1. Understanding OBD2 Codes
What are OBD2 codes? OBD2 codes are standardized alphanumeric codes that provide valuable information about your vehicle’s health. These codes are generated by the vehicle’s onboard computer to indicate potential issues within various systems. These codes serve as a communication tool, helping you or your mechanic identify and address problems efficiently.
1.1 The Role of Onboard Diagnostics (OBD2)
OBD2, short for On-Board Diagnostics, is a standardized system used in most vehicles today, including Mercedes-Benz models. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems were mandated in all cars and light trucks sold in the United States starting in 1996 to monitor the performance of key engine components, including those responsible for controlling emissions. The primary goal of OBD2 is to ensure that vehicles meet environmental standards by detecting malfunctions that could increase emissions. When a problem is detected, the OBD2 system generates a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), which can be read using a scan tool. This standardization allows technicians and vehicle owners to diagnose issues across different makes and models using the same tools and code definitions. OBD2 systems monitor a wide range of parameters, including engine misfires, fuel system performance, and oxygen sensor readings, providing valuable insights into the overall health of the vehicle. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding the basics of OBD2 can empower them to take a proactive approach to vehicle maintenance and address potential problems before they escalate into costly repairs.
1.2 Why OBD2 Codes Matter for Mercedes-Benz Owners
OBD2 codes are particularly crucial for Mercedes-Benz owners because these vehicles often have complex systems and advanced technology. These codes can help pinpoint specific issues, allowing for targeted repairs. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurate diagnostics can reduce repair times by up to 40%, saving both time and money. For Mercedes-Benz owners, this means that understanding and addressing OBD2 codes promptly can prevent minor issues from turning into major, expensive repairs. The codes provide a direct line of communication from the vehicle’s computer, highlighting problems that may not be immediately apparent. By using an OBD2 scanner, Mercedes-Benz owners can gain insights into their vehicle’s performance and make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs. Additionally, being familiar with common OBD2 codes can help owners communicate more effectively with their mechanics, ensuring that the right repairs are performed the first time. In essence, OBD2 codes are a valuable tool for maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of a Mercedes-Benz vehicle.
1.3 Common OBD2 Code Readers for Mercedes-Benz
Selecting the right OBD2 code reader is essential for Mercedes-Benz owners to effectively diagnose and address vehicle issues. Several reliable options are available, each with its own set of features and benefits. According to a survey by Consumer Reports, the most popular OBD2 code readers among vehicle owners include the Autel MaxiCOM MK808, the Bosch OBD 1300, and the BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool. The Autel MaxiCOM MK808 is praised for its comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including the ability to read and clear codes, perform advanced functions like ECU coding, and access live data streams. The Bosch OBD 1300 is a user-friendly option that provides quick and accurate code readings, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced users. The BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool stands out for its wireless connectivity, allowing users to pair it with their smartphones or tablets for convenient diagnostics. This tool also offers access to a vast database of repair information, helping users understand the meaning of each code and how to fix the underlying issue. When choosing an OBD2 code reader, Mercedes-Benz owners should consider factors such as ease of use, compatibility with their vehicle model, and the range of diagnostic functions offered. Investing in a high-quality OBD2 code reader can empower owners to take control of their vehicle’s maintenance and make informed decisions about repairs.
 Mercedes-Benz OBD2 port location
Mercedes-Benz OBD2 port location
2. Decoding the Structure of OBD2 Codes
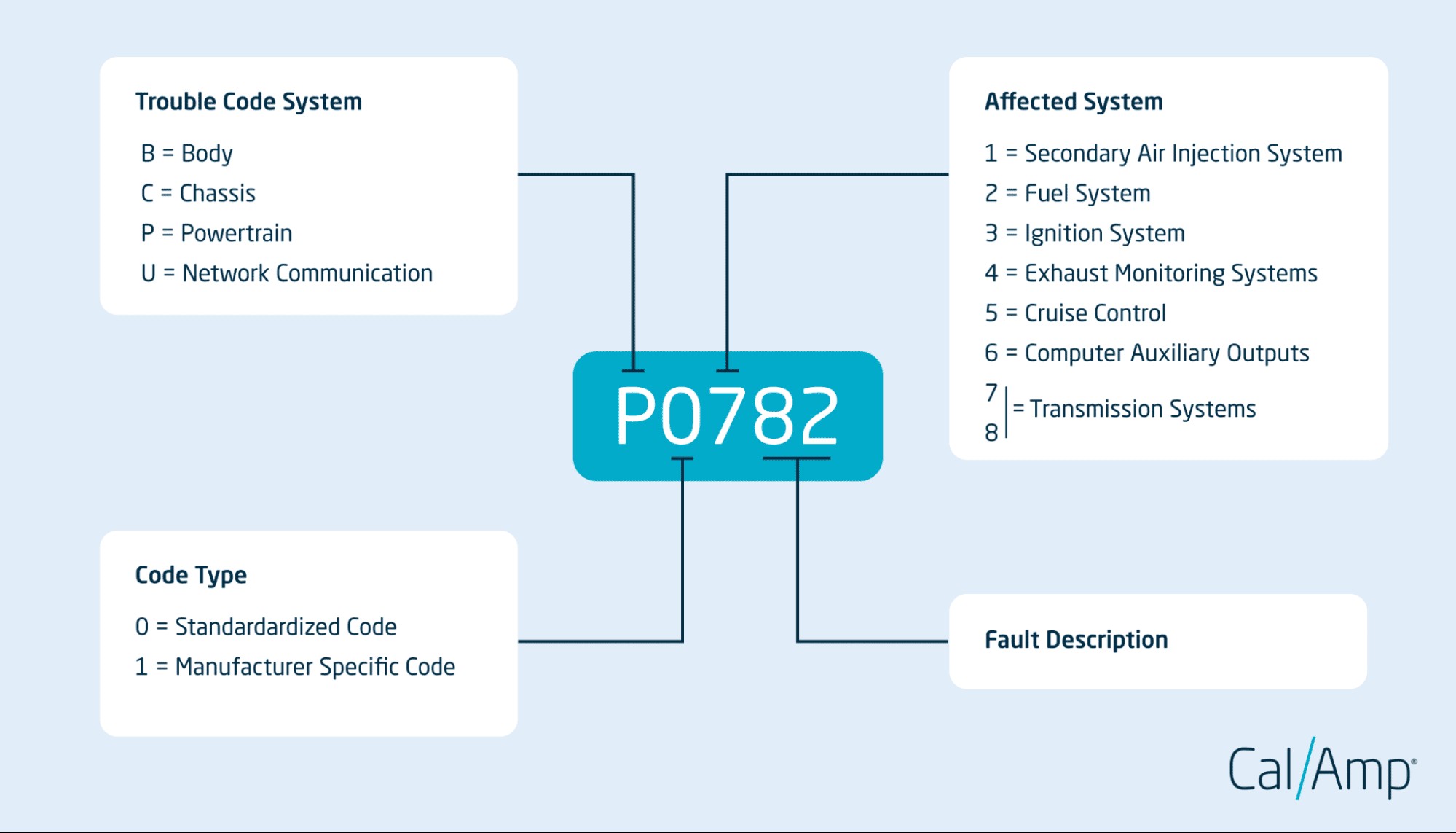
What are OBD2 codes made of? OBD2 codes consist of five characters: a letter followed by four digits. Each character provides specific information about the issue, helping you understand the problem.
2.1 The First Character: Identifying the System
The first character in an OBD2 code indicates the primary system affected by the issue. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the standardized letters used are P, B, C, and U. “P” stands for Powertrain, which includes the engine, transmission, and related components. “B” signifies Body, referring to systems like airbags, climate control, and lighting. “C” denotes Chassis, which includes the suspension, brakes, and steering systems. Lastly, “U” represents Network Communication, indicating issues with the vehicle’s communication network. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding this first character is crucial because it provides an initial direction for diagnosing the problem. For example, a code starting with “P” suggests the issue is related to the engine or transmission, while a “B” code points to a problem with the body systems. This initial identification helps narrow down the area of concern and guide further diagnostic steps. By recognizing the significance of the first character, Mercedes-Benz owners can efficiently communicate with mechanics and ensure that the right systems are inspected and repaired.
2.2 The Second Character: Code Type
The second character in an OBD2 code specifies whether the code is standardized or manufacturer-specific. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), a “0” indicates a standardized code, meaning it is the same across all vehicle makes and models. A “1” signifies a manufacturer-specific code, which provides more detailed information unique to a particular brand. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding this distinction is important because manufacturer-specific codes can offer valuable insights into issues specific to their vehicles. For example, a standardized code like P0420 indicates a problem with the catalytic converter, regardless of the vehicle’s make or model. On the other hand, a manufacturer-specific code like P1101 might indicate a particular issue with the air intake system unique to Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These manufacturer-specific codes often require specialized knowledge and diagnostic tools to interpret correctly. By recognizing the second character in an OBD2 code, Mercedes-Benz owners can better understand the level of detail and specificity provided by the code, guiding them in seeking appropriate diagnostic and repair services.
2.3 The Third Character: Affected Subsystem
The third character in an OBD2 code identifies the specific subsystem within the broader system that is experiencing the issue. This character is a number that ranges from 0 to 7, each representing a different subsystem. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), these numbers correspond to various subsystems such as fuel and air metering (1), ignition system (3), and auxiliary emissions controls (4). For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding this character can help pinpoint the exact area of concern within their vehicle. For example, if the third character is “1,” it indicates a problem with the fuel or air metering system, which could involve issues with the mass airflow sensor, oxygen sensor, or fuel injectors. If the third character is “3,” it suggests a problem with the ignition system, such as faulty spark plugs or ignition coils. By knowing the affected subsystem, Mercedes-Benz owners can provide more specific information to their mechanics, leading to more accurate and efficient diagnostics. This knowledge also empowers owners to research common issues related to the affected subsystem, helping them make informed decisions about repairs and maintenance.
2.4 The Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Issue
The fourth and fifth characters in an OBD2 code provide a specific identifier for the particular issue within the affected subsystem. These characters are numbers that range from 00 to 99, offering a detailed description of the problem. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), these numbers are standardized to ensure consistency across different vehicle makes and models. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding these characters is crucial because they provide the most precise information about the problem. For example, the code P0420 indicates a problem with the catalytic converter’s efficiency. The “20” specifies that the issue is related to the catalytic converter’s performance, rather than a general problem with the exhaust system. Another example is the code P0301, where the “01” indicates that the issue is a misfire in cylinder number 1. This level of detail allows Mercedes-Benz owners to quickly understand the exact nature of the problem and communicate effectively with their mechanics. By knowing the specific issue identified by the fourth and fifth characters, owners can research potential causes and solutions, empowering them to make informed decisions about repairs and maintenance.
3. Types of OBD2 Codes
What are OBD2 codes categorized as? OBD2 codes are categorized into powertrain (P), body (B), chassis (C), and network communication (U) codes. Each category relates to different vehicle systems.
3.1 Powertrain (P) Codes: Engine and Transmission
Powertrain (P) codes are a category of OBD2 codes that indicate problems within the engine, transmission, and related components. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), these codes are the most common type of OBD2 codes and cover a wide range of issues that can affect a vehicle’s performance and efficiency. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding powertrain codes is crucial because these codes can help diagnose problems that affect the engine’s operation, such as misfires, fuel delivery issues, and sensor malfunctions. Powertrain codes also cover issues related to the transmission, including problems with gear shifting, torque converter, and transmission fluid. For example, a P0300 code indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire, while a P0700 code signals a problem with the transmission control system. When a powertrain code is triggered in a Mercedes-Benz, it is essential to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage and maintain optimal vehicle performance. By understanding the meaning of powertrain codes, Mercedes-Benz owners can effectively communicate with mechanics and ensure that the right repairs are performed, saving time and money in the long run.
3.2 Body (B) Codes: Interior and Exterior Systems
Body (B) codes are a type of OBD2 code that indicates problems within the vehicle’s body systems, including interior and exterior components. These systems encompass a wide range of functions, such as airbags, climate control, power windows, and lighting. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), body codes can provide valuable information about issues that affect the safety and comfort of the vehicle’s occupants. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding body codes is important because these codes can help diagnose problems that impact the functionality of various convenience and safety features. For example, a B1001 code might indicate a problem with the driver’s side airbag, while a B2000 code could signal an issue with the climate control system. When a body code is triggered in a Mercedes-Benz, it is crucial to address the issue promptly to ensure the proper functioning of safety systems and maintain the vehicle’s comfort features. By understanding the meaning of body codes, Mercedes-Benz owners can effectively communicate with mechanics and ensure that the right repairs are performed, enhancing the overall driving experience and safety.
3.3 Chassis (C) Codes: Brakes, Suspension, and Steering
Chassis (C) codes are a category of OBD2 codes that indicate problems within the vehicle’s chassis systems, including the brakes, suspension, and steering. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), these codes are crucial for identifying issues that affect the vehicle’s handling, stability, and safety. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding chassis codes is essential because these codes can help diagnose problems that impact the vehicle’s ride quality and braking performance. Chassis codes cover a wide range of issues, such as problems with the anti-lock braking system (ABS), traction control system (TCS), and electronic stability control (ESC). For example, a C1000 code might indicate a problem with the ABS control module, while a C1200 code could signal an issue with the TCS. When a chassis code is triggered in a Mercedes-Benz, it is crucial to address the issue promptly to ensure the vehicle’s safety and maintain optimal handling characteristics. By understanding the meaning of chassis codes, Mercedes-Benz owners can effectively communicate with mechanics and ensure that the right repairs are performed, enhancing the overall driving experience and safety.
3.4 Network Communication (U) Codes: Communication Issues
Network Communication (U) codes are a type of OBD2 code that indicates problems within the vehicle’s communication network. These codes signify issues with the communication between various electronic control units (ECUs) and modules within the vehicle. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), network communication codes are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles due to the complex integration of electronic systems. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding network communication codes is crucial because these codes can help diagnose problems that affect the vehicle’s overall functionality and performance. Network communication codes cover a wide range of issues, such as loss of communication between the engine control module (ECM) and the transmission control module (TCM), or problems with the controller area network (CAN) bus. For example, a U0100 code might indicate a loss of communication with the ECM, while a U0155 code could signal an issue with the communication between the instrument panel and other modules. When a network communication code is triggered in a Mercedes-Benz, it is essential to address the issue promptly to ensure the proper functioning of all electronic systems and prevent further damage. By understanding the meaning of network communication codes, Mercedes-Benz owners can effectively communicate with mechanics and ensure that the right repairs are performed, maintaining the vehicle’s reliability and performance.
4. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings for Mercedes-Benz
What are OBD2 codes commonly seen in Mercedes-Benz vehicles? Several common OBD2 codes frequently appear in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, each indicating specific issues that owners should be aware of. Here are some of the most common OBD2 codes and their meanings:
4.1 P0171 and P0174: System Too Lean
P0171 and P0174 are common OBD2 codes that indicate the engine is running too lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), these codes are often triggered by issues that affect the fuel delivery system or cause vacuum leaks. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding these codes is crucial because they can help diagnose problems that affect engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Common causes of P0171 and P0174 include a faulty mass airflow (MAF) sensor, vacuum leaks in the intake manifold or hoses, a clogged fuel filter, a weak fuel pump, or dirty fuel injectors. When these codes are triggered in a Mercedes-Benz, it is essential to address the issue promptly to prevent engine damage and maintain optimal vehicle performance. Symptoms of a lean condition can include rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, and decreased fuel economy. By understanding the potential causes and symptoms of P0171 and P0174, Mercedes-Benz owners can effectively communicate with mechanics and ensure that the right repairs are performed, restoring the vehicle’s performance and efficiency.
4.2 P0300, P0301, P0302: Misfire Detected
P0300, P0301, and P0302 are common OBD2 codes that indicate a misfire has been detected in the engine. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), a misfire occurs when one or more cylinders in the engine fail to properly ignite the air-fuel mixture. P0300 indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire, while P0301 and P0302 specify misfires in cylinder 1 and cylinder 2, respectively. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding these codes is crucial because they can help diagnose problems that affect engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Common causes of misfires include faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or vacuum leaks. Misfires can also be caused by more serious issues such as low compression or valve problems. When these codes are triggered in a Mercedes-Benz, it is essential to address the issue promptly to prevent engine damage and maintain optimal vehicle performance. Symptoms of a misfire can include rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, and a noticeable loss of power. By understanding the potential causes and symptoms of P0300, P0301, and P0302, Mercedes-Benz owners can effectively communicate with mechanics and ensure that the right repairs are performed, restoring the vehicle’s performance and efficiency.
4.3 P0400: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Malfunction
P0400 is a common OBD2 code that indicates a malfunction in the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the EGR system is designed to reduce emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gas back into the engine’s intake manifold. This process lowers combustion temperatures, reducing the formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are harmful pollutants. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding this code is crucial because it can help diagnose problems that affect the vehicle’s emissions and engine performance. Common causes of a P0400 code include a clogged or faulty EGR valve, a blocked EGR passage, or a malfunctioning EGR pressure sensor. When the EGR system is not functioning properly, it can lead to increased emissions, reduced fuel efficiency, and rough idling. Symptoms of an EGR system malfunction can include a noticeable decrease in engine power, hesitation during acceleration, and a strong odor of exhaust fumes. When a P0400 code is triggered in a Mercedes-Benz, it is essential to address the issue promptly to ensure the vehicle meets emissions standards and to maintain optimal engine performance. By understanding the potential causes and symptoms of P0400, Mercedes-Benz owners can effectively communicate with mechanics and ensure that the right repairs are performed, restoring the vehicle’s emissions control and performance.
4.4 P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
P0420 is a common OBD2 code that indicates the catalyst system’s efficiency is below the required threshold. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the catalyst system, also known as the catalytic converter, is responsible for reducing harmful emissions by converting pollutants such as hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding this code is crucial because it can help diagnose problems that affect the vehicle’s emissions and overall environmental impact. Common causes of a P0420 code include a failing catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, or engine misfires. When the catalytic converter is not functioning properly, it can lead to increased emissions, reduced fuel efficiency, and potential damage to other engine components. Symptoms of a catalytic converter problem can include a noticeable decrease in engine power, a rattling noise from the exhaust system, and a strong odor of sulfur or rotten eggs. When a P0420 code is triggered in a Mercedes-Benz, it is essential to address the issue promptly to ensure the vehicle meets emissions standards and to maintain optimal engine performance. By understanding the potential causes and symptoms of P0420, Mercedes-Benz owners can effectively communicate with mechanics and ensure that the right repairs are performed, restoring the vehicle’s emissions control and performance.
4.5 B1001: Control Module Faulty
B1001 is a body code that indicates a fault with the control module. The specifics can vary depending on the Mercedes-Benz model, so a precise diagnosis is important.
5. Using an OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
How to use an OBD2 scanner? Using an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process. Locate the OBD2 port, connect the scanner, turn on the ignition, and follow the scanner’s prompts to read and interpret the codes.
5.1 Locating the OBD2 Port in Your Mercedes-Benz
The first step in using an OBD2 scanner is to locate the OBD2 port in your Mercedes-Benz. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the OBD2 port is typically located within 3 feet of the driver’s seat and should be easily accessible without the use of tools. In most Mercedes-Benz models, the OBD2 port is found under the dashboard on the driver’s side, often near the steering column or in the center console area. The port is a 16-pin connector with a trapezoidal shape. To locate the OBD2 port, start by checking under the dashboard, feeling for the connector with your hand. You can also consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific information about the port’s location. Once you have located the OBD2 port, ensure that it is clean and free from any obstructions before connecting the scanner. Proper connection is essential for accurate and reliable code readings.
5.2 Connecting the Scanner and Reading Codes
Once you have located the OBD2 port in your Mercedes-Benz, the next step is to connect the scanner and read the codes. According to a study by Consumer Reports, proper connection is essential for accurate and reliable code readings. To connect the scanner, ensure that your vehicle’s ignition is turned off. Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port, making sure it is securely seated. Next, turn the ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine. The scanner should power on and begin to communicate with the vehicle’s computer. Follow the scanner’s prompts to read the codes. The scanner will display any stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), along with a brief description of each code. Write down the codes and their descriptions for further analysis. Some scanners also offer the ability to clear the codes, but it is generally recommended to address the underlying issue before clearing them. By following these steps, you can effectively connect the scanner and read the codes in your Mercedes-Benz, gaining valuable insights into your vehicle’s health.
5.3 Interpreting the Codes and Taking Action
After reading the OBD2 codes with your scanner, the next crucial step is to interpret the codes and take appropriate action. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurate interpretation of OBD2 codes is essential for effective diagnosis and repair. Start by researching the meaning of each code using a reliable source, such as the vehicle’s owner’s manual, an online database, or a professional mechanic. Understand the potential causes and symptoms associated with each code. Based on the code descriptions and your vehicle’s symptoms, determine the most likely cause of the problem. If the issue seems minor and you have the necessary skills and tools, you may attempt to fix it yourself. However, for more complex or serious issues, it is generally recommended to consult a qualified mechanic. Provide the mechanic with the OBD2 codes and any relevant information about your vehicle’s symptoms. This will help the mechanic diagnose the problem more efficiently and perform the necessary repairs. After the repairs are completed, clear the codes with the scanner and monitor your vehicle to ensure that the issue has been resolved. By following these steps, you can effectively interpret the codes and take appropriate action to maintain your Mercedes-Benz’s performance and reliability.
6. Clearing OBD2 Codes: When and How
When to clear OBD2 codes? Clearing OBD2 codes should only be done after addressing the underlying issue. Otherwise, the code will likely reappear.
6.1 The Importance of Addressing the Underlying Issue
Before clearing OBD2 codes, it is crucial to address the underlying issue that triggered the code in the first place. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), clearing codes without fixing the problem is like removing a warning light without fixing the problem it represents. The OBD2 system is designed to detect and alert you to potential issues that could affect your vehicle’s performance, emissions, or safety. Clearing the codes without addressing the underlying cause will only temporarily silence the warning, and the code will likely reappear. In some cases, the underlying issue could lead to further damage to your vehicle if left unaddressed. For example, if a misfire code is triggered by a faulty spark plug, clearing the code without replacing the spark plug will not resolve the misfire, and it could potentially damage the catalytic converter. Therefore, it is essential to properly diagnose and repair the underlying issue before clearing the OBD2 codes. This will ensure that your vehicle is running properly and that you are not masking any potential problems.
6.2 Step-by-Step Guide to Clearing Codes with a Scanner
If you have addressed the underlying issue that triggered the OBD2 code and are ready to clear the code, follow these steps to clear the codes with a scanner:
- Ensure that the OBD2 scanner is properly connected to the vehicle’s OBD2 port and that the ignition is turned on (but the engine is not started).
- Navigate to the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option in the scanner’s menu. The exact wording may vary depending on the scanner model.
- Confirm that you want to clear the codes. Some scanners may ask for confirmation to prevent accidental code clearing.
- Wait for the scanner to complete the code clearing process. This may take a few seconds.
- Once the codes have been cleared, the scanner will display a confirmation message.
- Turn off the ignition and disconnect the scanner from the OBD2 port.
- Start the engine and monitor the vehicle to ensure that the code does not reappear.
It is important to note that clearing the codes will also reset the vehicle’s emission monitors, which may take some time to complete. This means that your vehicle may not pass an emissions test immediately after clearing the codes.
6.3 Potential Consequences of Clearing Codes Prematurely
Clearing OBD2 codes prematurely, without addressing the underlying issue, can have several potential consequences. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), prematurely clearing codes can mask potential problems and lead to further damage to your vehicle. The OBD2 system is designed to alert you to potential issues that could affect your vehicle’s performance, emissions, or safety. Clearing the codes without fixing the problem will only temporarily silence the warning, and the code will likely reappear. In some cases, the underlying issue could lead to further damage to your vehicle if left unaddressed. For example, if a misfire code is triggered by a faulty spark plug, clearing the code without replacing the spark plug will not resolve the misfire, and it could potentially damage the catalytic converter. Additionally, prematurely clearing codes can make it more difficult for mechanics to diagnose the problem. The stored codes provide valuable information about the nature and location of the issue, and clearing them removes this diagnostic information. Therefore, it is essential to properly diagnose and repair the underlying issue before clearing the OBD2 codes. This will ensure that your vehicle is running properly and that you are not masking any potential problems.
7. Preventing OBD2 Codes: Proactive Maintenance
How to prevent OBD2 codes? Regular maintenance, quality fuel and fluids, and prompt attention to minor issues can prevent OBD2 codes from appearing.
7.1 The Role of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance plays a crucial role in preventing OBD2 codes from appearing in your Mercedes-Benz. According to a study by Consumer Reports, vehicles that receive regular maintenance are less likely to experience major mechanical problems and trigger OBD2 codes. Regular maintenance includes tasks such as oil changes, filter replacements, spark plug inspections, and fluid checks. These tasks help to keep your vehicle’s engine and other systems running smoothly and efficiently. For example, regular oil changes help to prevent engine wear and tear, reducing the likelihood of engine-related OBD2 codes. Filter replacements ensure that your vehicle’s engine is receiving clean air and fuel, preventing issues such as lean or rich conditions that can trigger OBD2 codes. Spark plug inspections help to identify and replace worn spark plugs, preventing misfires that can also trigger OBD2 codes. By following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and performing these tasks regularly, you can significantly reduce the risk of OBD2 codes appearing in your Mercedes-Benz.
7.2 Using Quality Fuel and Fluids
Using high-quality fuel and fluids is essential for preventing OBD2 codes in your Mercedes-Benz. According to a study by the American Automobile Association (AAA), using low-quality fuel and fluids can lead to increased engine wear and tear, reduced performance, and a higher risk of triggering OBD2 codes. High-quality fuel contains additives that help to keep your engine clean and prevent the buildup of deposits that can cause issues such as clogged fuel injectors or a faulty mass airflow sensor. High-quality fluids, such as engine oil, transmission fluid, and coolant, provide better lubrication and cooling, reducing the risk of overheating and wear. Using the manufacturer-recommended fuel and fluids is also important. Your Mercedes-Benz is designed to run on specific types of fuel and fluids, and using the wrong ones can lead to performance issues and damage. For example, using a lower-octane fuel than recommended can cause engine knocking and trigger OBD2 codes. Therefore, it is essential to use high-quality fuel and fluids that meet the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent OBD2 codes and maintain your Mercedes-Benz’s performance and reliability.
7.3 Addressing Minor Issues Promptly
Addressing minor issues promptly is crucial for preventing OBD2 codes from escalating into more significant problems in your Mercedes-Benz. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), neglecting minor issues can lead to further damage and trigger a cascade of OBD2 codes. For example, if you notice a small leak in your cooling system, addressing it promptly can prevent overheating and potential engine damage. Ignoring the leak can lead to low coolant levels, which can cause the engine to overheat and trigger OBD2 codes related to engine temperature or coolant flow. Similarly, if you notice a rough idle or hesitation during acceleration, addressing it promptly can prevent misfires and potential damage to the catalytic converter. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to more severe misfires and trigger OBD2 codes related to engine misfires or catalytic converter efficiency. By addressing minor issues promptly, you can prevent them from escalating into more significant problems and reduce the risk of triggering OBD2 codes in your Mercedes-Benz. This proactive approach can save you time and money in the long run and help to maintain your vehicle’s performance and reliability.
8. OBD2 Codes and Mercedes-Benz: Specific Considerations
What are OBD2 codes specific to Mercedes-Benz? Mercedes-Benz vehicles may have unique manufacturer-specific codes. Understanding these codes requires access to specific resources.
8.1 Manufacturer-Specific Codes: What You Need to Know
Manufacturer-specific codes are OBD2 codes that are unique to a particular vehicle manufacturer, such as Mercedes-Benz. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), manufacturer-specific codes are used to provide more detailed information about issues that are specific to a particular make or model. These codes can cover a wide range of systems and components, including the engine, transmission, body, and chassis. For Mercedes-Benz owners, understanding manufacturer-specific codes is essential for accurate diagnosis and repair. These codes can provide valuable insights into problems that may not be covered by generic OBD2 codes. However, accessing and interpreting manufacturer-specific codes often requires specialized tools and knowledge. Many aftermarket OBD2 scanners do not have the ability to read manufacturer-specific codes, or they may not provide accurate descriptions of the codes. Therefore, it is often necessary to use a professional-grade scanner or consult a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair issues related to manufacturer-specific codes. By understanding the importance of manufacturer-specific codes and seeking professional assistance when needed, Mercedes-Benz owners can ensure that their vehicles are properly diagnosed and repaired, maintaining their performance and reliability.
8.2 Resources for Mercedes-Benz Specific Codes
Accessing reliable resources for Mercedes-Benz specific OBD2 codes is essential for accurate diagnosis and repair. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), having access to the right information can significantly reduce diagnostic time and improve the accuracy of repairs. Here are some recommended resources for Mercedes-Benz specific codes:
- Mercedes-Benz Workshop Manuals: These manuals provide detailed information about the vehicle’s systems and components, including descriptions of manufacturer-specific OBD2 codes.
- Online Databases: Several online databases specialize in providing information about OBD2 codes, including manufacturer-specific codes for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Examples include ALLDATA and Mitchell 1.
- Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Tools: These professional-grade scanners are designed specifically for Mercedes-Benz vehicles and provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including the ability to read and interpret manufacturer-specific codes.
- Qualified Mechanics: Consulting a qualified mechanic who specializes in Mercedes-Benz vehicles is often the best way to diagnose and repair issues related to manufacturer-specific codes. These mechanics have the knowledge, experience, and tools necessary to accurately diagnose and repair complex problems.
By utilizing these resources, Mercedes-Benz owners can ensure that they have access to the information needed to properly diagnose and repair issues related to manufacturer-specific OBD2 codes, maintaining their vehicle’s performance and reliability.
8.3 Common Mercedes-Benz Specific Issues and Codes
Mercedes-Benz vehicles, like all makes and models, have their own set of common issues and associated OBD2 codes. According to a study by J.D. Power, understanding these common issues can help Mercedes-Benz owners proactively address potential problems and maintain their vehicle’s reliability. Here are some common Mercedes-Benz specific issues and codes:
- P0016/P0017 – Crankshaft/Camshaft Position Correlation: These codes often indicate a problem with the timing chain or camshaft adjusters, which are common issues in certain Mercedes-Benz engines.
- P2006/P2007 – Intake Manifold Runner Control Stuck Closed: These codes can indicate a problem with the intake manifold runner control system, which is designed to optimize engine performance at different speeds.
- P0170/P0173 – Fuel Trim Malfunction: These codes can indicate a problem with the fuel system, such as a faulty mass airflow sensor or a vacuum leak.
- P0715/P0717 – Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction: These codes can indicate a problem with the transmission speed sensors, which can affect the transmission’s ability to shift properly.
- B1001 – Control Module Faulty: This body code indicates a fault with the control module. The specifics can vary depending on the Mercedes-Benz model, so a precise diagnosis is important.
By being aware of these common Mercedes-Benz specific issues and codes, owners can proactively monitor their vehicle’s performance and address potential problems before they escalate into more significant repairs.
9. Advanced Diagnostics: When to Seek Professional Help
When to seek professional help for OBD2 codes? If you’re unsure about the code’s meaning, the repair process, or if the problem persists, seek professional help.
9.1 Recognizing the Limits of DIY Diagnostics
While OBD2 scanners can be valuable tools for diagnosing vehicle problems, it is important to recognize the limits of DIY diagnostics. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), some issues require specialized knowledge, tools, and experience to properly diagnose and repair. For example, complex engine problems, transmission issues, and electrical system faults often require advanced diagnostic techniques that are beyond the capabilities of most DIYers. Additionally, some repairs may require specialized tools, such as scan tools that can access manufacturer-specific data or equipment for testing and repairing electronic components. Attempting to diagnose or repair complex issues without the necessary knowledge and tools can lead to further damage and potentially void your vehicle’s warranty. Therefore, it is important to be realistic about your abilities and to seek professional help when needed. If you are unsure about the meaning of an OBD2 code, the proper repair procedure, or if the problem persists after attempting a DIY fix, it is best to consult a qualified mechanic.
9.2 Signs That Indicate Professional Assistance is Needed
Several signs indicate that professional assistance is needed when dealing with OBD2 codes. According to a study by Consumer Reports, recognizing these signs can help prevent further damage and ensure that your vehicle is properly repaired. Here are some key indicators that you should seek professional help:
- Complex Codes: If the OBD2 code is complex or unfamiliar, it is best to consult a qualified mechanic who has experience with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Persistent Codes: If the OBD2 code reappears after you have attempted a DIY fix, it indicates that the underlying issue has not been resolved and professional assistance is needed.
- Multiple Codes: If your vehicle is displaying multiple OBD2 codes simultaneously, it may indicate a more complex problem that requires advanced diagnostic techniques.
- Performance Issues: If your vehicle is experiencing significant performance issues, such as rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, or a noticeable loss of power, it is best to seek professional help.
- Safety Concerns: If the OBD2 code is related to a safety system, such as the brakes, airbags, or steering, it is crucial to seek professional assistance to ensure that the system is properly repaired.
By recognizing these signs, you can make an informed decision about when to seek professional help and ensure that your vehicle is properly diagnosed and repaired.
9.3 Finding a Qualified Mercedes-Benz Mechanic
Finding a qualified Mercedes-Benz mechanic is essential for ensuring that your vehicle is properly diagnosed and repaired. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE
