How Can Diagnostic Tools Be Used To Program New TPMS Sensors? Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) diagnostic tools are essential for programming new sensors, ensuring proper vehicle safety and performance, and MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides the resources you need to master this process. Using advanced diagnostic equipment allows technicians and car enthusiasts alike to efficiently replace and configure TPMS sensors, ultimately enhancing vehicle maintenance and diagnostic capabilities. Explore sensor programming, automotive diagnostics, and TPMS relearn procedures to optimize your vehicle’s tire management system.
Contents
- 1. Understanding TPMS and Its Importance
- 1.1 What is TPMS?
- 1.2 Why is TPMS Important?
- 1.3 Legal Requirements
- 2. The Evolution of TPMS Technology
- 2.1 Early TPMS Systems
- 2.2 Advancements in TPMS Technology
- 2.3 The Role of Diagnostic Tools
- 3. Types of TPMS Sensors
- 3.1 OEM Sensors
- 3.2 Aftermarket Sensors
- 3.3 Universal Sensors
- 4. Diagnostic Tools for TPMS Programming
- 4.1 Basic TPMS Tools
- 4.2 Advanced TPMS Tools
- 4.3 Multi-Functional Diagnostic Scanners
- 5. Key Features to Look for in a TPMS Diagnostic Tool
- 5.1 Vehicle Coverage
- 5.2 Sensor Compatibility
- 5.3 Ease of Use
- 5.4 Update Capability
- 5.5 OBDII Connectivity
- 5.6 Programming Options
- 6. Step-by-Step Guide: Programming New TPMS Sensors
- 6.1 Preparation
- 6.2 Removing the Old Sensor
- 6.3 Installing the New Sensor
- 6.4 Programming the New Sensor
- 6.5 Performing a Relearn Procedure
- 6.6 Final Checks
- 7. Common TPMS Issues and Troubleshooting
- 7.1 TPMS Light Stays On
- 7.2 Sensor Not Transmitting
- 7.3 Incorrect Pressure Readings
- 7.4 TPMS Light Flashing
- 7.5 Interference
- 8. Best Practices for TPMS Maintenance
- 8.1 Regular Inspections
- 8.2 Sensor Replacement
- 8.3 Proper Inflation
- 8.4 Professional Service
- 9. Advanced TPMS Diagnostic Techniques
- 9.1 Using OBDII Data
- 9.2 Analyzing Waveforms
- 9.3 Performing System Tests
- 10. Benefits of Using Advanced Diagnostic Tools for TPMS
- 10.1 Improved Accuracy
- 10.2 Enhanced Efficiency
- 10.3 Comprehensive Diagnostics
- 10.4 Cost Savings
- 11. TPMS Relearn Procedures Explained
- 11.1 What is a TPMS Relearn Procedure?
- 11.2 Types of Relearn Procedures
- 11.3 Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Relearn Procedure
- 12. Choosing the Right TPMS Sensor for Your Vehicle
- 12.1 OEM vs. Aftermarket Sensors
- 12.2 Direct-Fit vs. Programmable Sensors
- 12.3 Considerations for Choosing a Sensor
- 13. The Future of TPMS Technology
- 13.1 Advancements in Sensor Technology
- 13.2 Integration with Vehicle Systems
- 13.3 The Role of Data Analytics
- 14. Understanding TPMS Sensor Battery Life
- 14.1 Factors Affecting Battery Life
- 14.2 Signs of a Weak Battery
- 14.3 Replacing Sensors with Weak Batteries
- 15. DIY vs. Professional TPMS Service
- 15.1 DIY TPMS Service
- 15.2 Professional TPMS Service
- 15.3 When to Choose DIY vs. Professional Service
- 16. How TPMS Affects Vehicle Performance and Safety
- 16.1 Impact on Handling
- 16.2 Impact on Braking
- 16.3 Impact on Fuel Efficiency
- 16.4 Impact on Tire Wear
- 17. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz TPMS
- 17.1 Specific Considerations for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 17.2 Recommended TPMS Tools for Mercedes-Benz
- 17.3 Step-by-Step Guide to TPMS Reset on Mercedes-Benz
- 18. Expert Tips for TPMS Programming and Maintenance
- 18.1 Read the Vehicle’s Service Manual
- 18.2 Use High-Quality Sensors
- 18.3 Calibrate Regularly
- 18.4 Inspect Sensors Regularly
- 18.5 Stay Updated
- 19. Resources for Further Learning
- 19.1 Online Courses and Tutorials
- 19.2 Industry Publications
- 19.3 Professional Organizations
- 20. Why Choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your TPMS Needs?
- FAQ: Programming TPMS Sensors
- 1. What is a TPMS sensor and what does it do?
- 2. Why is it necessary to program new TPMS sensors?
- 3. What tools are needed to program new TPMS sensors?
- 4. Can I program TPMS sensors myself, or do I need a professional?
- 5. How often should TPMS sensors be replaced?
- 6. What is a TPMS relearn procedure and why is it important?
- 7. Are there different types of TPMS relearn procedures?
- 8. What should I do if the TPMS warning light stays on after programming new sensors?
- 9. How can I choose the right TPMS sensor for my vehicle?
- 10. Where can I find reliable TPMS programming and maintenance services?
1. Understanding TPMS and Its Importance
1.1 What is TPMS?
Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) is an electronic system designed to monitor the air pressure inside the tires on various types of vehicles. TPMS reports real-time tire-pressure information to the driver of the vehicle, either via a gauge, a pictogram display, or a simple low-pressure warning light. TPMS can be direct or indirect. Direct TPMS employs pressure sensors inside the tires, while indirect TPMS monitors tire pressure by using the vehicle’s anti-lock braking system’s (ABS) wheel speed sensors. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), TPMS has been proven to reduce the risk of accidents caused by underinflated tires.
1.2 Why is TPMS Important?
Maintaining correct tire pressure is crucial for several reasons:
- Safety: Underinflated tires can lead to tire failure, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Fuel Efficiency: Properly inflated tires reduce rolling resistance, improving fuel economy. The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that you can improve your gas mileage by up to 3% by keeping your tires inflated to the proper pressure.
- Tire Life: Correct tire pressure ensures even wear, extending the lifespan of your tires.
- Vehicle Handling: Optimal tire pressure provides better handling and stability, particularly in emergency situations.
1.3 Legal Requirements
In many countries, including the United States, TPMS is a mandatory safety feature on all new passenger vehicles. The TREAD Act, enacted in 2000, mandated the use of TPMS in vehicles to reduce the number of accidents caused by tire failure.
2. The Evolution of TPMS Technology
2.1 Early TPMS Systems
The earliest TPMS systems were relatively simple, primarily designed to alert drivers to significant pressure loss in one or more tires. These systems often lacked the precision and detailed information provided by modern TPMS.
2.2 Advancements in TPMS Technology
Over the years, TPMS technology has significantly advanced. Modern TPMS offers:
- Direct Pressure Readings: Real-time display of tire pressure for each tire.
- Temperature Monitoring: Some systems also monitor tire temperature.
- Sensor Identification: Ability to identify individual sensors and their locations.
- Wireless Communication: Wireless transmission of data from sensors to the vehicle’s computer.
2.3 The Role of Diagnostic Tools
The evolution of TPMS has been closely linked to the development of diagnostic tools. Early tools could only read sensor data, but modern tools can:
- Activate Sensors: Trigger sensors to transmit data.
- Read Sensor Data: Display pressure, temperature, and sensor ID.
- Program New Sensors: Configure replacement sensors to work with the vehicle.
- Perform Relearn Procedures: Reset the TPMS system after sensor replacement.
3. Types of TPMS Sensors
3.1 OEM Sensors
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) sensors are those installed in the vehicle at the factory. They are designed to work seamlessly with the vehicle’s TPMS system. OEM sensors are generally considered to be the most reliable, but they can also be the most expensive.
3.2 Aftermarket Sensors
Aftermarket sensors are replacement sensors manufactured by companies other than the vehicle manufacturer. They are typically less expensive than OEM sensors and can be either:
- Direct-Fit: Pre-programmed to work with specific vehicle makes and models.
- Programmable: Blank sensors that can be programmed to match the vehicle’s TPMS system.
3.3 Universal Sensors
Universal sensors are programmable sensors designed to work with a wide range of vehicles. They offer greater flexibility and can reduce the need to stock multiple types of sensors.
4. Diagnostic Tools for TPMS Programming
4.1 Basic TPMS Tools
These tools are primarily used for reading sensor data and activating sensors. They are suitable for basic TPMS maintenance and troubleshooting.
4.2 Advanced TPMS Tools
Advanced TPMS tools offer more comprehensive features, including:
- Sensor Programming: Ability to program new sensors.
- OBDII Communication: Communication with the vehicle’s computer through the OBDII port.
- Relearn Procedures: Automated reset of the TPMS system.
- Diagnostic Functions: Additional diagnostic capabilities for TPMS-related issues.
4.3 Multi-Functional Diagnostic Scanners
These scanners combine TPMS functions with other diagnostic capabilities, such as reading and clearing trouble codes, performing system tests, and accessing vehicle data.
5. Key Features to Look for in a TPMS Diagnostic Tool
5.1 Vehicle Coverage
Ensure the tool supports the makes and models of vehicles you will be servicing. A comprehensive vehicle coverage list is essential for versatility.
5.2 Sensor Compatibility
Verify the tool is compatible with the types of sensors you will be using (OEM, aftermarket, universal).
5.3 Ease of Use
Look for a tool with an intuitive interface, clear instructions, and a user-friendly design.
5.4 Update Capability
Choose a tool that can be easily updated with the latest vehicle and sensor data. Regular updates are crucial for maintaining accuracy and compatibility.
5.5 OBDII Connectivity
OBDII connectivity allows the tool to communicate with the vehicle’s computer, enabling advanced functions such as relearn procedures and diagnostic tests.
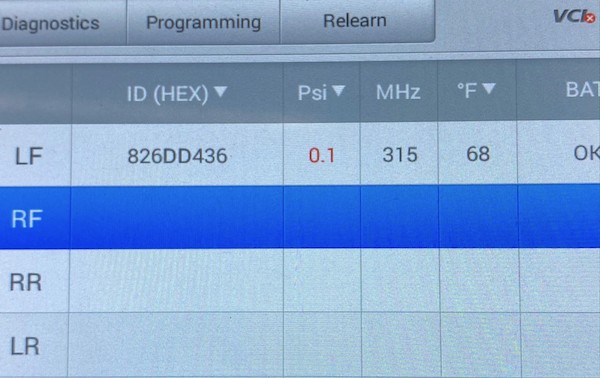
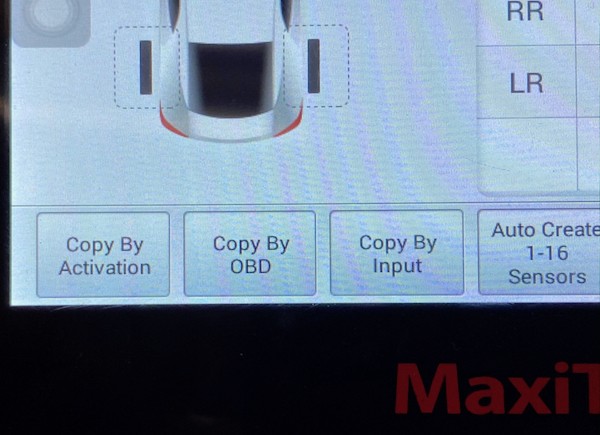
5.6 Programming Options
The tool should offer various programming options, including:
- Automatic ID Creation: Generating new sensor IDs.
- Manual ID Input: Entering sensor IDs manually.
- ID Cloning: Copying IDs from old sensors to new sensors.
6. Step-by-Step Guide: Programming New TPMS Sensors
6.1 Preparation
- Gather Necessary Tools and Equipment: TPMS diagnostic tool, new TPMS sensors, tire changing equipment, and a vehicle service manual.
- Check the Vehicle’s TPMS System: Use the diagnostic tool to read the existing sensor data and identify any issues.
- Ensure Compatibility: Verify that the new sensors are compatible with the vehicle and the diagnostic tool.
6.2 Removing the Old Sensor
- Deflate the Tire: Completely deflate the tire before removing it from the wheel.
- Disassemble the Tire from the Wheel: Use a tire changing machine to carefully remove the tire from the wheel.
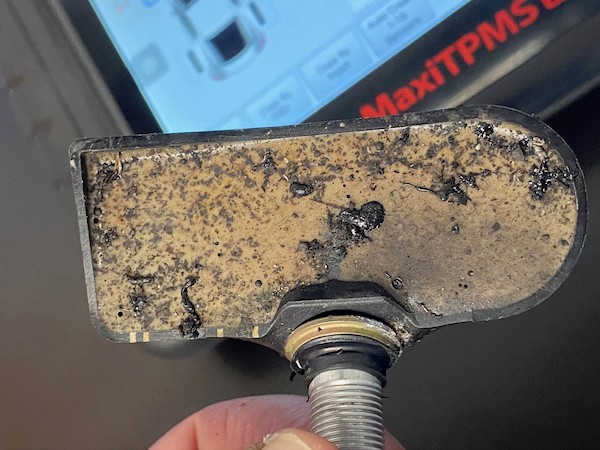
- Remove the Old Sensor: Unscrew and remove the old TPMS sensor from the wheel.
6.3 Installing the New Sensor
- Install the New Sensor: Mount the new TPMS sensor onto the wheel, ensuring it is properly seated and tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reassemble the Tire to the Wheel: Carefully reassemble the tire onto the wheel using the tire changing machine.
- Inflate the Tire: Inflate the tire to the recommended pressure specified in the vehicle’s owner’s manual.
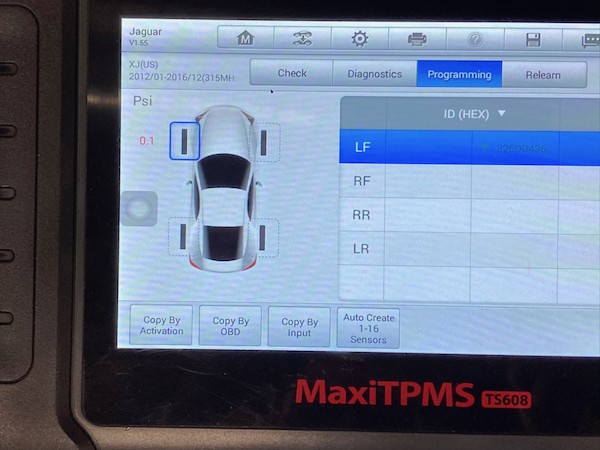
6.4 Programming the New Sensor
- Connect the Diagnostic Tool: Plug the TPMS diagnostic tool into the vehicle’s OBDII port.
- Power On the Tool and Select the Vehicle: Follow the tool’s instructions to select the correct vehicle make, model, and year.
- Enter TPMS Programming Mode: Navigate to the TPMS programming section of the tool’s menu.
- Choose Programming Method: Select the appropriate programming method (automatic ID creation, manual ID input, or ID cloning).
- Program the Sensor: Follow the tool’s prompts to program the new sensor. This may involve entering the sensor ID manually or allowing the tool to generate a new ID.
- Verify Programming: Use the tool to verify that the sensor has been successfully programmed and is transmitting data.
6.5 Performing a Relearn Procedure
- Initiate Relearn Procedure: Follow the diagnostic tool’s instructions to initiate the TPMS relearn procedure.
- Follow Relearn Steps: The relearn procedure may involve driving the vehicle for a certain distance or performing a specific sequence of actions.
- Verify Relearn Completion: Use the tool to verify that the relearn procedure has been successfully completed and that the TPMS light is off.
6.6 Final Checks
- Check Tire Pressure: Ensure all tires are inflated to the recommended pressure.
- Test the TPMS System: Take the vehicle for a short test drive to ensure the TPMS system is functioning correctly.
- Clear Trouble Codes: Use the diagnostic tool to clear any TPMS-related trouble codes from the vehicle’s computer.
 TPMS Diagnostic Tool
TPMS Diagnostic Tool
7. Common TPMS Issues and Troubleshooting
7.1 TPMS Light Stays On
- Problem: The TPMS warning light remains illuminated even after inflating the tires to the correct pressure.
- Possible Causes: Faulty sensor, incorrect sensor programming, TPMS system malfunction.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Use a diagnostic tool to read sensor data and identify any issues. Check sensor batteries, wiring, and connections. Perform a TPMS relearn procedure.
7.2 Sensor Not Transmitting
- Problem: One or more sensors are not transmitting data to the vehicle’s computer.
- Possible Causes: Dead sensor battery, damaged sensor, interference.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Use a diagnostic tool to activate the sensor and check for a response. Replace the sensor if necessary.
7.3 Incorrect Pressure Readings
- Problem: The TPMS displays incorrect tire pressure readings.
- Possible Causes: Faulty sensor, calibration issue, interference.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Use a diagnostic tool to compare the TPMS readings with a manual pressure gauge. Calibrate the TPMS system if necessary. Replace the sensor if it is faulty.
7.4 TPMS Light Flashing
- Problem: The TPMS warning light is flashing.
- Possible Causes: System malfunction, sensor compatibility issue.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Use a diagnostic tool to read trouble codes and diagnose the issue. Ensure that the sensors are compatible with the vehicle.
7.5 Interference
- Problem: The TPMS system experiences interference, leading to incorrect readings or communication issues.
- Possible Causes: Electronic devices, radio frequency interference.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Identify and remove any potential sources of interference. Ensure that the TPMS system is properly shielded.
8. Best Practices for TPMS Maintenance
8.1 Regular Inspections
Inspect the TPMS sensors and system regularly to identify any potential issues. Check for damage, corrosion, and loose connections.
8.2 Sensor Replacement
Replace TPMS sensors every 5-7 years or when replacing tires. Sensor batteries have a limited lifespan and will eventually fail.
8.3 Proper Inflation
Maintain the correct tire pressure as specified in the vehicle’s owner’s manual. Check and adjust tire pressure regularly, especially with changes in temperature.
8.4 Professional Service
Consult a professional technician for TPMS maintenance and repairs. They have the expertise and equipment to properly diagnose and resolve TPMS issues.
 Tire Pressure Check
Tire Pressure Check
9. Advanced TPMS Diagnostic Techniques
9.1 Using OBDII Data
Advanced TPMS tools can access OBDII data to diagnose TPMS-related issues. This includes reading trouble codes, accessing sensor data, and performing system tests.
9.2 Analyzing Waveforms
Some diagnostic tools can analyze TPMS sensor waveforms to identify subtle issues. This technique requires advanced training and expertise.
9.3 Performing System Tests
Advanced TPMS tools can perform system tests to verify the functionality of the TPMS system. These tests may include sensor activation, pressure simulation, and communication tests.
10. Benefits of Using Advanced Diagnostic Tools for TPMS
10.1 Improved Accuracy
Advanced diagnostic tools provide more accurate and reliable TPMS readings, leading to better maintenance and troubleshooting.
10.2 Enhanced Efficiency
Advanced tools can automate TPMS programming and relearn procedures, saving time and effort.
10.3 Comprehensive Diagnostics
Advanced tools offer comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, allowing technicians to identify and resolve a wider range of TPMS issues.
10.4 Cost Savings
By accurately diagnosing and resolving TPMS issues, advanced tools can help prevent costly repairs and replacements.
11. TPMS Relearn Procedures Explained
11.1 What is a TPMS Relearn Procedure?
A TPMS relearn procedure is the process of resetting the TPMS system after replacing or reprogramming sensors. This procedure allows the vehicle’s computer to recognize the new sensor IDs and monitor tire pressure correctly.
11.2 Types of Relearn Procedures
- Auto Relearn: The vehicle automatically learns the new sensor IDs after driving for a certain distance or time.
- Manual Relearn: The relearn procedure requires a specific sequence of actions, such as inflating and deflating tires in a specific order.
- OBD Relearn: The relearn procedure requires the use of a diagnostic tool to communicate with the vehicle’s computer through the OBDII port.
11.3 Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Relearn Procedure
- Consult the Vehicle’s Service Manual: Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the specific relearn procedure.
- Prepare the Vehicle: Ensure the vehicle is parked on a level surface and the ignition is turned off.
- Initiate Relearn Procedure: Follow the instructions in the service manual or the diagnostic tool to initiate the relearn procedure.
- Follow Relearn Steps: Perform the required sequence of actions, such as driving the vehicle or inflating and deflating tires.
- Verify Relearn Completion: Use the diagnostic tool to verify that the relearn procedure has been successfully completed and that the TPMS light is off.
 TPMS Sensor Installation
TPMS Sensor Installation
12. Choosing the Right TPMS Sensor for Your Vehicle
12.1 OEM vs. Aftermarket Sensors
- OEM Sensors: Designed to work seamlessly with the vehicle’s TPMS system, but can be more expensive.
- Aftermarket Sensors: Less expensive than OEM sensors, but may require programming.
12.2 Direct-Fit vs. Programmable Sensors
- Direct-Fit Sensors: Pre-programmed to work with specific vehicle makes and models.
- Programmable Sensors: Blank sensors that can be programmed to match the vehicle’s TPMS system.
12.3 Considerations for Choosing a Sensor
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure the sensor is compatible with the vehicle make, model, and year.
- Sensor Type: Choose the appropriate sensor type (OEM, aftermarket, direct-fit, programmable).
- Quality and Reliability: Select a sensor from a reputable manufacturer to ensure quality and reliability.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the sensor and the cost of programming (if required).
13. The Future of TPMS Technology
13.1 Advancements in Sensor Technology
Future TPMS sensors may offer:
- Extended Battery Life: Longer sensor battery life to reduce the need for frequent replacements.
- Improved Accuracy: More accurate and reliable pressure readings.
- Enhanced Functionality: Additional features, such as tire temperature monitoring and wear detection.
13.2 Integration with Vehicle Systems
TPMS may become more integrated with other vehicle systems, such as:
- Adaptive Cruise Control: Adjusting vehicle speed based on tire pressure and road conditions.
- Electronic Stability Control: Enhancing vehicle stability by monitoring tire pressure.
- Autonomous Driving Systems: Providing critical data for autonomous driving systems.
13.3 The Role of Data Analytics
TPMS data may be used for data analytics to:
- Predict Tire Failures: Identifying patterns and predicting potential tire failures.
- Optimize Tire Maintenance: Providing recommendations for tire maintenance and replacement.
- Improve Vehicle Performance: Enhancing vehicle performance by optimizing tire pressure and alignment.
14. Understanding TPMS Sensor Battery Life
14.1 Factors Affecting Battery Life
TPMS sensor batteries typically last for 5-7 years, but several factors can affect their lifespan:
- Usage: Frequent driving and exposure to extreme temperatures can shorten battery life.
- Climate: Extreme heat and cold can accelerate battery degradation.
- Sensor Quality: Higher-quality sensors tend to have longer battery life.
14.2 Signs of a Weak Battery
- Intermittent TPMS Warnings: The TPMS warning light may appear and disappear intermittently.
- Inaccurate Readings: The TPMS may display inaccurate tire pressure readings.
- Sensor Not Transmitting: The sensor may stop transmitting data altogether.
14.3 Replacing Sensors with Weak Batteries
It is essential to replace TPMS sensors with weak batteries to ensure proper TPMS functionality. Ignoring a weak battery can lead to inaccurate readings and potential safety issues.
15. DIY vs. Professional TPMS Service
15.1 DIY TPMS Service
- Pros: Cost savings, convenience.
- Cons: Requires technical knowledge, specialized tools, and potential for errors.
15.2 Professional TPMS Service
- Pros: Expertise, specialized equipment, and guaranteed results.
- Cons: Higher cost, requires scheduling an appointment.
15.3 When to Choose DIY vs. Professional Service
- DIY: Suitable for basic TPMS maintenance, such as checking tire pressure and replacing sensors.
- Professional Service: Recommended for complex TPMS issues, such as sensor programming, relearn procedures, and system diagnostics.
16. How TPMS Affects Vehicle Performance and Safety
16.1 Impact on Handling
Properly inflated tires improve vehicle handling and stability, particularly in emergency situations. Underinflated tires can reduce handling and increase the risk of accidents.
16.2 Impact on Braking
Correct tire pressure optimizes braking performance and reduces stopping distances. Underinflated tires can increase braking distances and compromise safety.
16.3 Impact on Fuel Efficiency
Properly inflated tires reduce rolling resistance, improving fuel economy. Underinflated tires increase rolling resistance and reduce fuel efficiency.
16.4 Impact on Tire Wear
Correct tire pressure ensures even wear, extending the lifespan of your tires. Underinflated or overinflated tires can lead to uneven wear and premature tire failure.
17. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz TPMS
17.1 Specific Considerations for Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Mercedes-Benz vehicles often use advanced TPMS systems that require specific diagnostic tools and procedures. It is essential to use a TPMS tool that is compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles and to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
17.2 Recommended TPMS Tools for Mercedes-Benz
- Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis: A comprehensive diagnostic tool designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Autel MaxiTPMS TS508: A versatile TPMS tool that supports Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- ATEQ VT56: A professional-grade TPMS tool that is compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
17.3 Step-by-Step Guide to TPMS Reset on Mercedes-Benz
- Check Tire Pressure: Ensure all tires are inflated to the recommended pressure.
- Start the Engine: Start the vehicle’s engine.
- Access TPMS Menu: Navigate to the TPMS menu on the vehicle’s display screen.
- Select “Reset” or “Calibrate”: Choose the appropriate option to reset or calibrate the TPMS system.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the reset procedure.
- Verify Completion: Verify that the TPMS light is off and that the system is functioning correctly.
18. Expert Tips for TPMS Programming and Maintenance
18.1 Read the Vehicle’s Service Manual
Always consult the vehicle’s service manual for specific TPMS procedures and recommendations.
18.2 Use High-Quality Sensors
Invest in high-quality TPMS sensors from reputable manufacturers to ensure reliability and longevity.
18.3 Calibrate Regularly
Calibrate the TPMS system regularly to maintain accuracy, especially after replacing tires or sensors.
18.4 Inspect Sensors Regularly
Inspect TPMS sensors regularly for damage, corrosion, and loose connections.
18.5 Stay Updated
Stay updated on the latest TPMS technology and diagnostic procedures.
 Rapid Deflation Test
Rapid Deflation Test
19. Resources for Further Learning
19.1 Online Courses and Tutorials
- ATEQ TPMS Training: Offers comprehensive TPMS training courses and tutorials.
- Bartec USA TPMS Training: Provides online training resources for TPMS programming and diagnostics.
19.2 Industry Publications
- Tire Review: A leading industry publication covering tire technology and maintenance.
- Underhood Service: A trade magazine for automotive technicians.
19.3 Professional Organizations
- Tire Industry Association (TIA): A professional organization for the tire industry.
- Automotive Service Association (ASA): A professional organization for automotive service professionals.
20. Why Choose MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your TPMS Needs?
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the intricacies of TPMS systems in Mercedes-Benz vehicles and offer expert guidance and solutions to ensure your vehicle’s safety and performance. Whether you’re looking to diagnose a TPMS issue, program new sensors, or simply maintain your system, our comprehensive resources and knowledgeable staff are here to help. Contact us today to learn more about how we can assist you with your TPMS needs.
Address: 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Don’t hesitate to reach out for expert advice and top-notch service!
FAQ: Programming TPMS Sensors
1. What is a TPMS sensor and what does it do?
A TPMS sensor is an electronic device that monitors the air pressure inside a vehicle’s tires and transmits this data to the vehicle’s computer, alerting the driver to any significant pressure loss.
2. Why is it necessary to program new TPMS sensors?
Programming new TPMS sensors is necessary to ensure that the vehicle’s computer recognizes the new sensor IDs and can accurately monitor tire pressure.
3. What tools are needed to program new TPMS sensors?
You will need a TPMS diagnostic tool, new TPMS sensors, tire changing equipment, and a vehicle service manual.
4. Can I program TPMS sensors myself, or do I need a professional?
While it is possible to program TPMS sensors yourself, it requires technical knowledge, specialized tools, and the potential for errors. Professional service is recommended for complex TPMS issues.
5. How often should TPMS sensors be replaced?
TPMS sensors should be replaced every 5-7 years or when replacing tires, as their batteries have a limited lifespan.
6. What is a TPMS relearn procedure and why is it important?
A TPMS relearn procedure is the process of resetting the TPMS system after replacing or reprogramming sensors, allowing the vehicle’s computer to recognize the new sensor IDs and monitor tire pressure correctly.
7. Are there different types of TPMS relearn procedures?
Yes, there are auto relearn, manual relearn, and OBD relearn procedures. The type of procedure depends on the vehicle make and model.
8. What should I do if the TPMS warning light stays on after programming new sensors?
Use a diagnostic tool to read sensor data and identify any issues. Check sensor batteries, wiring, and connections. Perform a TPMS relearn procedure.
9. How can I choose the right TPMS sensor for my vehicle?
Ensure the sensor is compatible with the vehicle make, model, and year. Choose the appropriate sensor type (OEM, aftermarket, direct-fit, programmable) and select a sensor from a reputable manufacturer.
10. Where can I find reliable TPMS programming and maintenance services?
At MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer expert guidance and solutions to ensure your vehicle’s safety and performance. Contact us today for assistance with your TPMS needs.