Live data can be used to monitor alternator output and battery voltage, offering invaluable insights into your Mercedes-Benz’s charging system health and overall performance; MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to guide you. Leveraging real-time data streams empowers you to diagnose potential issues proactively, ensuring optimal battery and alternator performance while preventing unexpected breakdowns, and the related diagnostic adaptations, sensor data analysis, and system performance evaluation.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Importance of Monitoring Alternator Output and Battery Voltage
- 1.1 Why Monitor Alternator Output?
- 1.2 Why Monitor Battery Voltage?
- 1.3 Interaction Between Alternator and Battery
- 2. Tools and Techniques for Monitoring Live Data
- 2.1 Multimeters
- 2.2 OBD-II Scanners
- 2.2.1 Basic OBD-II Scanners
- 2.2.2 Advanced OBD-II Scanners
- 2.2.3 Mercedes-Specific Scanners
- 2.3 Using Scan Tools to Access Live Data
- 2.4 Smartphone Apps and Bluetooth Adapters
- 3. Interpreting Live Data Readings
- 3.1 Normal Alternator Output Voltage
- 3.2 Normal Battery Voltage
- 3.3 Factors Affecting Alternator Output and Battery Voltage
- 3.4 Common Issues Indicated by Live Data
- 4. Case Studies: Using Live Data for Diagnosis
- 4.1 Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Faulty Alternator
- 4.2 Case Study 2: Identifying a Failing Voltage Regulator
- 4.3 Case Study 3: Detecting a Parasitic Draw
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Monitoring Alternator Output and Battery Voltage
- 6. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 7.1 Voltage Drop Testing
- 7.2 Current Draw Testing
- 7.3 Waveform Analysis
- 8. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz Charging System
- 8.1 Battery Maintenance
- 8.2 Alternator Maintenance
- 8.3 Professional Inspection
- 9. Upgrading Your Mercedes-Benz Charging System
- 9.1 High-Output Alternators
- 9.2 Upgraded Batteries
- 9.3 Wiring Upgrades
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Understanding the Importance of Monitoring Alternator Output and Battery Voltage
Monitoring alternator output and battery voltage is crucial for maintaining the health and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz. A well-functioning charging system ensures that the battery remains adequately charged, powering all electrical components and preventing breakdowns. Understanding why these parameters are important and how they interact can help you proactively address potential issues before they escalate.
1.1 Why Monitor Alternator Output?
The alternator is the heart of your vehicle’s electrical system, responsible for generating power to run electrical components while the engine is running and for recharging the battery. Monitoring its output is critical for several reasons:
-
Preventing Battery Drain: A faulty alternator may not produce enough power to keep the battery charged, leading to a gradual drain and potential failure.
-
Ensuring Optimal Performance: Insufficient alternator output can affect the performance of various electrical systems, such as the headlights, air conditioning, and infotainment system.
-
Avoiding Costly Repairs: Identifying alternator issues early can prevent damage to other components, such as the battery and voltage regulator, saving you money on extensive repairs.
1.2 Why Monitor Battery Voltage?
Battery voltage is an indicator of the battery’s state of charge and overall health. Monitoring battery voltage is essential for:
-
Detecting Charging System Issues: Abnormal voltage readings can indicate problems with the alternator, voltage regulator, or battery itself.
-
Preventing Starting Problems: A low battery voltage can result in difficulty starting the engine, especially in cold weather.
-
Extending Battery Life: Maintaining the correct voltage levels can prevent overcharging or undercharging, both of which can shorten the battery’s lifespan.
1.3 Interaction Between Alternator and Battery
The alternator and battery work together to provide electrical power to your vehicle. The alternator generates power, which is then used to charge the battery and run electrical components. The battery acts as a reserve, providing power when the engine is off or when the alternator cannot meet the demand. Monitoring both components allows you to assess the overall health and efficiency of the charging system. According to a study by the Battery Council International, proper maintenance of both the alternator and battery can extend the lifespan of the battery by up to two years.
2. Tools and Techniques for Monitoring Live Data
To effectively monitor alternator output and battery voltage, you need the right tools and techniques. Several options are available, ranging from basic multimeters to advanced diagnostic scanners. Understanding the capabilities of each tool will help you choose the best option for your needs.
2.1 Multimeters
A multimeter is a versatile tool that can measure voltage, current, and resistance. It is a fundamental tool for diagnosing electrical issues in vehicles. To use a multimeter for monitoring alternator output and battery voltage:
-
Battery Voltage Test: Set the multimeter to DC voltage mode and connect the probes to the battery terminals. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts when the engine is off.
-
Alternator Output Test: With the engine running, the voltage should increase to around 14 volts, indicating that the alternator is charging the battery.
-
Load Test: Turn on various electrical loads, such as headlights and air conditioning, and observe the voltage drop. Excessive voltage drop may indicate an alternator issue.
While a multimeter is useful for basic measurements, it provides limited real-time data and does not offer the advanced diagnostic capabilities of a scan tool.
2.2 OBD-II Scanners
OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanners are devices that connect to your vehicle’s diagnostic port and retrieve data from the engine control unit (ECU). These scanners can display live data, including alternator output, battery voltage, engine speed, and other parameters.
2.2.1 Basic OBD-II Scanners
These scanners offer basic diagnostic functions and can read and clear trouble codes. They also typically display live data streams, allowing you to monitor alternator output and battery voltage in real-time.
2.2.2 Advanced OBD-II Scanners
Advanced scanners provide more sophisticated features, such as graphing, data logging, and bidirectional control. These scanners are useful for in-depth diagnostics and can help you identify intermittent issues that may not be apparent with a basic scanner.
2.2.3 Mercedes-Specific Scanners
For Mercedes-Benz vehicles, specialized scanners offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities. These scanners can access proprietary diagnostic codes and data streams, providing more detailed information about the charging system and other vehicle systems. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of Mercedes-specific scanners tailored to meet the needs of both DIY enthusiasts and professional technicians.
2.3 Using Scan Tools to Access Live Data
To use a scan tool to access live data:
-
Connect the scanner to the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard.
-
Turn on the ignition but do not start the engine.
-
Navigate to the live data or data stream menu.
-
Select the parameters you want to monitor, such as alternator voltage, battery voltage, and engine speed.
-
Start the engine and observe the data streams in real-time.
-
Record the data for further analysis or troubleshooting.
2.4 Smartphone Apps and Bluetooth Adapters
Another option for monitoring live data is to use a smartphone app in conjunction with a Bluetooth OBD-II adapter. These adapters plug into the OBD-II port and transmit data to your smartphone via Bluetooth. Various apps are available that can display live data, read trouble codes, and perform other diagnostic functions.
This setup offers convenience and portability, allowing you to monitor your vehicle’s charging system on the go. However, the capabilities of these apps may vary, so it is essential to choose one that meets your specific needs.
 Communication Device Gadget Telephony Portable communications device Material property
Communication Device Gadget Telephony Portable communications device Material property
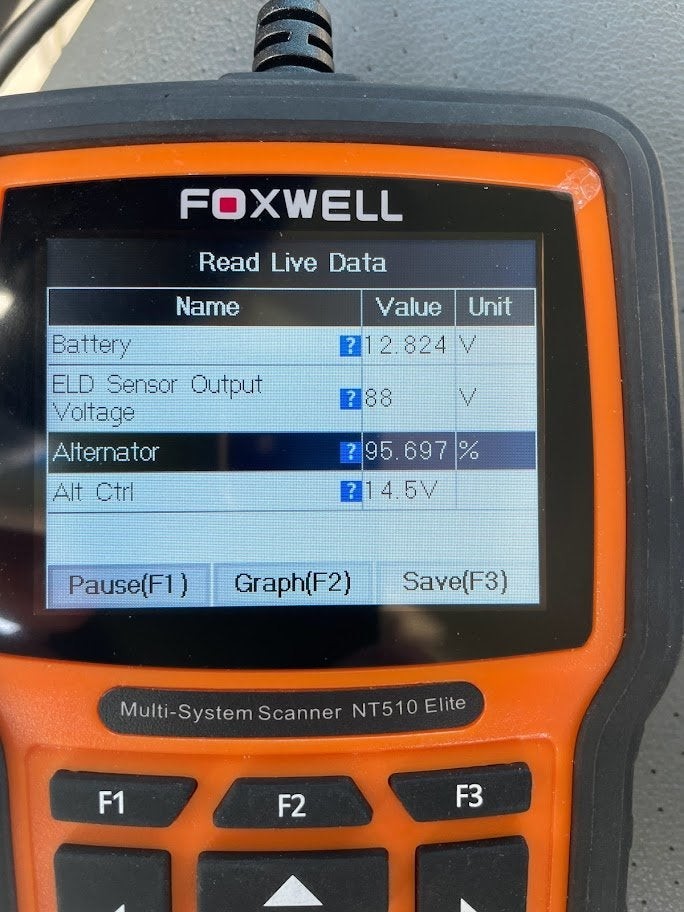
3. Interpreting Live Data Readings
Once you have access to live data, the next step is to interpret the readings and identify potential issues. Understanding the normal ranges for alternator output and battery voltage, as well as the factors that can affect these parameters, is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
3.1 Normal Alternator Output Voltage
The normal alternator output voltage typically ranges from 13.5 to 14.5 volts when the engine is running. This voltage level is necessary to charge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical components.
- Low Voltage: If the alternator output voltage is below 13.5 volts, it may indicate a problem with the alternator, voltage regulator, or wiring.
- High Voltage: If the alternator output voltage is above 14.5 volts, it may indicate a faulty voltage regulator, which can lead to overcharging and damage to the battery.
3.2 Normal Battery Voltage
The normal battery voltage should be around 12.6 volts when the engine is off. When the engine is running, the voltage should increase to around 14 volts, indicating that the alternator is charging the battery.
- Low Voltage: If the battery voltage is below 12.0 volts, it may indicate a discharged or failing battery.
- High Voltage: If the battery voltage is consistently above 14.5 volts, it may indicate overcharging, which can damage the battery.
3.3 Factors Affecting Alternator Output and Battery Voltage
Several factors can affect alternator output and battery voltage, including:
- Engine Speed: Alternator output typically increases with engine speed. At idle, the alternator may produce less power than at higher RPMs.
- Electrical Load: The more electrical components that are turned on, the higher the load on the alternator. This can cause the voltage to drop, especially at idle.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect battery performance. Cold temperatures can reduce battery capacity, while hot temperatures can accelerate battery degradation.
- Battery Age: As batteries age, their capacity decreases, and they may not hold a charge as well as new batteries.
- Wiring and Connections: Corroded or loose wiring and connections can cause voltage drops and affect the performance of the charging system.
3.4 Common Issues Indicated by Live Data
Interpreting live data can help you identify various issues with the charging system:
- Low Alternator Output at Idle: This may indicate a worn alternator or a problem with the voltage regulator.
- Excessive Voltage Drop Under Load: This may indicate an alternator that cannot keep up with the electrical demand, or a failing battery.
- Fluctuating Voltage Readings: This may indicate a loose connection or a faulty voltage regulator.
- Consistently High or Low Battery Voltage: This may indicate a problem with the alternator, voltage regulator, or battery itself.
According to a study by the SAE International, monitoring live data can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40% compared to traditional diagnostic methods.
4. Case Studies: Using Live Data for Diagnosis
To illustrate how live data can be used to diagnose charging system issues, consider the following case studies:
4.1 Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Faulty Alternator
A customer complains that their Mercedes-Benz battery keeps dying, even after being jump-started. Using a scan tool, you access live data and observe the following:
- Battery voltage with the engine off: 12.2 volts
- Alternator output voltage at idle: 13.0 volts
- Alternator output voltage at 2000 RPM: 13.2 volts
These readings indicate that the alternator is not producing enough voltage to charge the battery properly. Further testing confirms that the alternator is faulty and needs to be replaced.
4.2 Case Study 2: Identifying a Failing Voltage Regulator
A customer reports that their Mercedes-Benz battery is constantly being overcharged. Using a scan tool, you access live data and observe the following:
- Battery voltage with the engine off: 12.7 volts
- Alternator output voltage at idle: 15.5 volts
- Alternator output voltage at 2000 RPM: 16.0 volts
These readings indicate that the voltage regulator is not functioning correctly, causing the alternator to overcharge the battery. Replacing the voltage regulator resolves the issue.
4.3 Case Study 3: Detecting a Parasitic Draw
A customer complains that their Mercedes-Benz battery drains overnight, even when the vehicle is not in use. Using a multimeter, you measure the current draw with the engine off and find that it is significantly higher than the normal parasitic draw (typically less than 50 milliamps).
By systematically disconnecting circuits and monitoring the current draw, you identify a faulty module that is causing the parasitic draw. Replacing the module resolves the issue.
 Hood Light Product Luggage and bags Bag
Hood Light Product Luggage and bags Bag
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Monitoring Alternator Output and Battery Voltage
To effectively monitor alternator output and battery voltage, follow these steps:
-
Gather Your Tools: You will need a multimeter or an OBD-II scanner, along with any necessary adapters or cables.
-
Prepare the Vehicle: Park the vehicle on a level surface and turn off all accessories, such as headlights, air conditioning, and the radio.
-
Connect the Tool: Connect the multimeter or OBD-II scanner to the appropriate terminals or port.
-
Monitor Battery Voltage (Engine Off): With the engine off, measure the battery voltage. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts.
-
Start the Engine: Start the engine and allow it to idle.
-
Monitor Alternator Output Voltage: With the engine running, measure the alternator output voltage. It should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
-
Perform a Load Test: Turn on various electrical loads, such as headlights and air conditioning, and observe the voltage drop. The voltage should not drop below 13.0 volts.
-
Record Your Findings: Record all voltage readings and any other relevant data.
-
Analyze the Data: Compare your readings to the normal ranges and identify any potential issues.
-
Troubleshoot and Repair: Based on your findings, troubleshoot and repair any issues with the charging system.
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid
When monitoring alternator output and battery voltage, it is essential to avoid common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate diagnoses:
-
Using a Low-Quality Multimeter or Scanner: Investing in a high-quality tool is essential for accurate readings and reliable performance.
-
Not Following the Manufacturer’s Instructions: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for using your multimeter or scanner.
-
Ignoring Safety Precautions: When working with electrical systems, it is crucial to take safety precautions, such as wearing gloves and eye protection.
-
Not Considering All Factors: Be sure to consider all factors that can affect alternator output and battery voltage, such as engine speed, electrical load, and temperature.
-
Misinterpreting the Data: Take the time to understand the normal ranges for alternator output and battery voltage, and how to interpret abnormal readings.
7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
In addition to basic monitoring, advanced diagnostic techniques can provide more in-depth insights into the charging system’s performance.
7.1 Voltage Drop Testing
Voltage drop testing involves measuring the voltage drop across various circuits to identify areas of high resistance. Excessive voltage drop can indicate corroded connections, damaged wiring, or faulty components.
To perform a voltage drop test:
-
Connect the multimeter to the circuit you want to test.
-
Turn on the electrical load.
-
Measure the voltage drop across the circuit.
-
Compare the voltage drop to the manufacturer’s specifications.
-
Identify and repair any areas of excessive voltage drop.
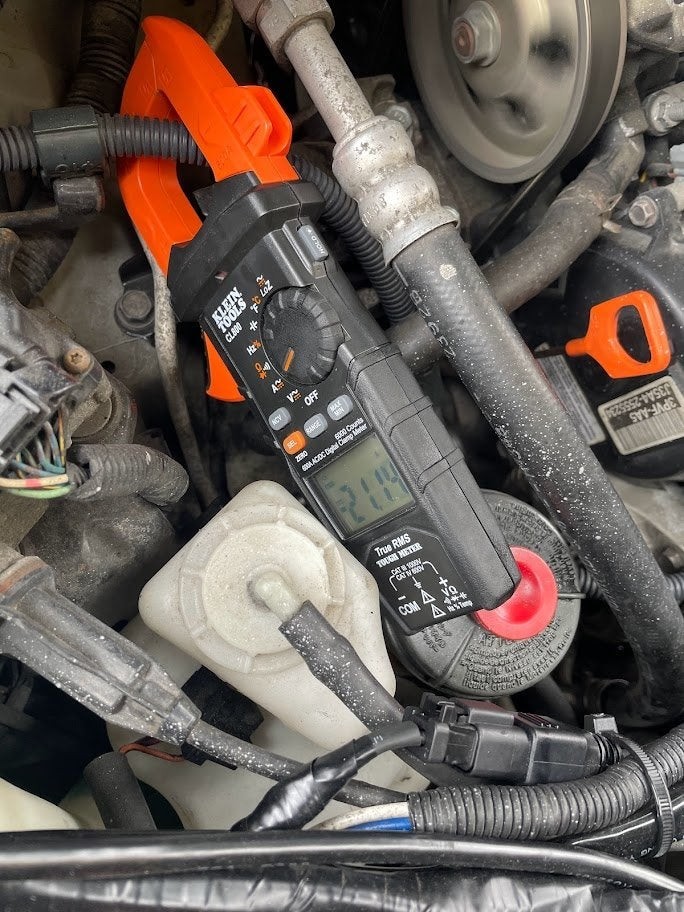
7.2 Current Draw Testing
Current draw testing involves measuring the amount of current being drawn by various circuits to identify parasitic draws or other electrical issues.
To perform a current draw test:
-
Disconnect the negative battery cable.
-
Connect the multimeter in series with the negative battery cable.
-
Measure the current draw with the engine off and all accessories turned off.
-
Compare the current draw to the manufacturer’s specifications.
-
Identify and troubleshoot any excessive current draws.
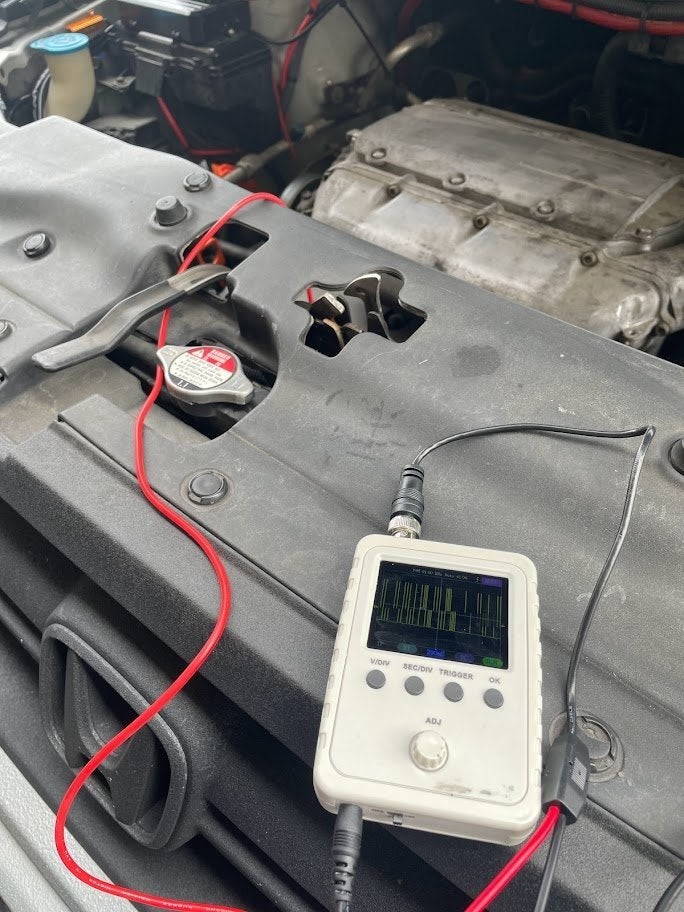
7.3 Waveform Analysis
Waveform analysis involves using an oscilloscope to analyze the voltage and current waveforms of the alternator and other electrical components. This can help you identify intermittent issues or subtle problems that may not be apparent with other diagnostic methods.
According to a study by the Automotive Service Association, advanced diagnostic techniques can improve diagnostic accuracy by up to 30%.
 Motor vehicle Hood Automotive design Automotive exterior Auto part
Motor vehicle Hood Automotive design Automotive exterior Auto part
8. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz Charging System
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term health and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz charging system.
8.1 Battery Maintenance
- Keep the Battery Clean: Clean the battery terminals and connections regularly to prevent corrosion.
- Check the Electrolyte Level: If your battery has removable caps, check the electrolyte level regularly and add distilled water as needed.
- Test the Battery Regularly: Have your battery tested regularly to assess its state of charge and overall health.
8.2 Alternator Maintenance
- Inspect the Alternator Belt: Check the alternator belt for wear and tear, and replace it as needed.
- Check the Wiring and Connections: Inspect the wiring and connections to the alternator for corrosion and damage.
- Test the Alternator Output Regularly: Monitor the alternator output voltage regularly to identify potential issues early.
8.3 Professional Inspection
Schedule regular inspections with a qualified technician to ensure that your charging system is functioning correctly. A professional can perform a comprehensive inspection and identify any potential issues before they escalate. MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can connect you with experienced technicians who specialize in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
9. Upgrading Your Mercedes-Benz Charging System
If you frequently experience charging system issues or if you have added aftermarket electrical components that increase the electrical demand, you may want to consider upgrading your charging system.
9.1 High-Output Alternators
High-output alternators can provide more power to meet the demands of aftermarket electrical components, such as high-powered audio systems, lighting upgrades, and other accessories.
9.2 Upgraded Batteries
Upgraded batteries, such as AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries, offer increased capacity and improved performance compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
9.3 Wiring Upgrades
Upgrading the wiring can improve the efficiency of the charging system and reduce voltage drops. This is especially important when installing a high-output alternator or adding aftermarket electrical components.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the normal battery voltage for a Mercedes-Benz?
A1: The normal battery voltage for a Mercedes-Benz is around 12.6 volts when the engine is off and between 13.5 and 14.5 volts when the engine is running.
Q2: How can I check my alternator output voltage?
A2: You can check your alternator output voltage using a multimeter or an OBD-II scanner. Connect the tool to the appropriate terminals or port and measure the voltage with the engine running.
Q3: What does it mean if my battery voltage is too low?
A3: If your battery voltage is too low, it may indicate a discharged or failing battery, a faulty alternator, or a parasitic draw.
Q4: What does it mean if my alternator output voltage is too high?
A4: If your alternator output voltage is too high, it may indicate a faulty voltage regulator, which can lead to overcharging and damage to the battery.
Q5: How often should I have my charging system inspected?
A5: You should have your charging system inspected at least once a year or whenever you notice any signs of charging system issues.
Q6: Can I replace my alternator myself?
A6: Replacing an alternator can be a challenging task, especially on a Mercedes-Benz. If you are not comfortable working on electrical systems, it is best to have a qualified technician perform the replacement.
Q7: What is a parasitic draw?
A7: A parasitic draw is an excessive amount of current being drawn from the battery when the engine is off and all accessories are turned off. This can drain the battery overnight and cause starting problems.
Q8: How can I find a qualified technician to work on my Mercedes-Benz charging system?
A8: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can connect you with experienced technicians who specialize in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
Q9: What are the benefits of upgrading my charging system?
A9: Upgrading your charging system can provide more power to meet the demands of aftermarket electrical components, improve the efficiency of the charging system, and reduce voltage drops.
Q10: Where can I find reliable diagnostic tools for my Mercedes-Benz?
A10: MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of Mercedes-specific diagnostic tools tailored to meet the needs of both DIY enthusiasts and professional technicians.
Monitoring alternator output and battery voltage is crucial for maintaining the health and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz. By using the right tools and techniques, interpreting the data accurately, and performing regular maintenance, you can ensure that your charging system is functioning correctly and prevent unexpected breakdowns. Remember, MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is your trusted partner in keeping your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly.
Experiencing charging system issues or unsure how to interpret the live data from your Mercedes-Benz? Contact us at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert advice and assistance. Our team of Mercedes-Benz specialists is ready to help you diagnose and resolve any charging system problems. Reach out today at 789 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at MERCEDES-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information and to explore our range of diagnostic tools and services.